Thermodynamics influences many aspects of our lives, from cooking to refrigeration, making it a vital field of study. By grasping these principles, we can enhance our energy efficiency and comfort. For instance, understanding thermodynamic processes can inspire creative design, such as mug mockups that reflect everyday applications.
Thermodynamics, a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and energy, is not just an academic subject but plays a crucial role in our daily lives. From cooking food to driving cars, the principles of thermodynamics are all around us. Understanding these principles can lead to more efficient energy use and enhanced comfort in everyday activities. In this article, we will explore various applications of thermodynamics in our daily routines and how a better understanding of these principles can improve our lives.
Understanding the Basics of Thermodynamics
Before delving into practical applications, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental laws of thermodynamics:
- First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
- Second Law of Thermodynamics: In any energy transfer, the total entropy (disorder) of a closed system can never decrease over time.
- Third Law of Thermodynamics: As temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a perfect crystal approaches zero.
Everyday Applications of Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics manifests in various everyday applications, influencing how we interact with our environment. Here are some practical instances:
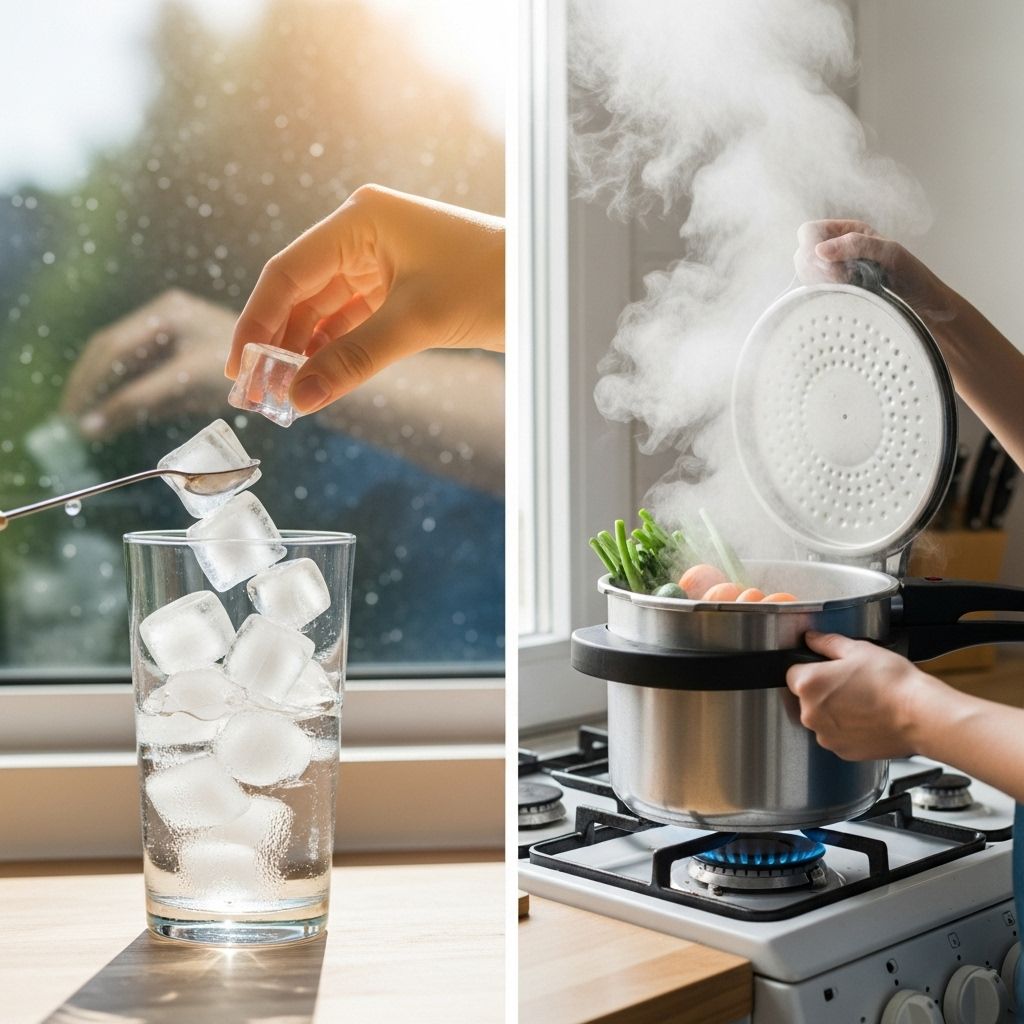
1. Cooking
Cooking is a perfect example of thermodynamics in action. When you heat food, you’re transferring energy to it, which changes its chemical and physical properties.
- Conduction: Heat transfer through direct contact (e.g., a pot on a stove).
- Convection: Heat transfer through fluids (e.g., boiling water).
- Radiation: Heat transfer through electromagnetic waves (e.g., a microwave oven).
2. Refrigeration
The principle of refrigeration is grounded in the laws of thermodynamics, notably the refrigerant cycle. Refrigerators and air conditioners utilize the second law of thermodynamics to remove heat from a cooler space and expel it into a warmer one, thereby keeping our food fresh and our living spaces comfortable.
3. Automobiles
Cars operate based on the principles of thermodynamics. Internal combustion engines convert fuel energy into mechanical energy, using the first law of thermodynamics. Here’s how:
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Intake Stroke | Air and fuel enter the combustion chamber. |
| Compression Stroke | The mixture is compressed, increasing its temperature and pressure. |
| Power Stroke | Ignition happens, causing an explosion that drives the piston. |
| Exhaust Stroke | Exhaust gases are expelled from the chamber. |
4. Home Heating and Cooling
Heating systems, such as furnaces and boilers, and cooling systems, like air conditioners, rely on thermodynamic principles to maintain comfortable indoor environments.
- Furnaces burn fuel to generate heat, which is then distributed by convection through the home.
- Air conditioners use the refrigeration cycle to absorb heat from indoors and release it outside.
Energy Efficiency and Conservation
Understanding thermodynamics helps promote energy efficiency and conservation in daily life. Here are some strategies:
1. Insulation
Proper insulation in homes reduces heat loss in winter and keeps cool air inside during summer. This practice minimizes energy consumption:
- Use double-glazed windows.
- Insulate walls and roofs.
- Seal leaks around doors and windows.
2. Energy-Efficient Appliances
Selecting appliances that adhere to energy-efficient standards can significantly reduce energy consumption:
- Refrigerators: Look for models with high energy ratings.
- Washing Machines: Use water-efficient models to save both energy and water.
3. Smart Home Technology
Integrating smart technology can enhance energy efficiency:
- Smart thermostats adjust home temperatures based on occupancy.
- Energy monitoring systems provide insights into consumption patterns, enabling users to make informed decisions.
The Future of Thermodynamics in Everyday Life
The relevance of thermodynamics in daily life is only set to grow, particularly with advancements in technology and sustainability efforts. Here’s a glimpse into potential future applications:
1. Renewable Energy Sources
Thermodynamics is crucial in harnessing renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal energy:
- Solar Panels: Convert sunlight into electrical energy using photovoltaic cells.
- Wind Turbines: Use kinetic energy from wind to generate power.
- Geothermal Systems: Utilize heat from the Earth for heating and electricity generation.
2. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The rise of electric vehicles showcases a shift in thermodynamic applications. EVs convert electrical energy to mechanical energy efficiently:
- Regenerative braking systems recover energy during braking, enhancing overall energy efficiency.
- Battery technology advancements improve energy storage capabilities.
3. Smart Grids
Smart grids leverage thermodynamic principles to optimize electricity distribution, leading to more efficient energy use:
- Real-time monitoring of energy consumption patterns.
- Integration of renewable energy sources into the grid.
Conclusion
From cooking to transportation and energy conservation, thermodynamics influences every facet of our daily lives. By understanding and applying these principles, we can enhance our energy efficiency, reduce costs, and contribute to a more sustainable future. The ongoing advancements in technology promise to further integrate thermodynamic principles into even more aspects of our daily routine, paving the way for a smarter, energy-efficient world.
FAQ
How can I use thermodynamics when cooking?
Thermodynamics plays a crucial role in cooking by explaining how heat transfer affects food. For example, understanding heat conduction helps you use the right cooking methods, like frying or boiling, to achieve the desired texture and flavor.
What is the role of thermodynamics in refrigeration?
Thermodynamics is fundamental in refrigeration as it explains how heat is removed from the interior of the refrigerator to keep food fresh. The refrigeration cycle utilizes principles of thermodynamics to transfer heat efficiently.
How does thermodynamics apply to everyday appliances?
Most household appliances, such as air conditioners and heaters, rely on thermodynamic principles to regulate temperature and energy efficiency, ensuring comfort and reducing energy consumption.
Can thermodynamics help me save energy at home?
Yes, by understanding thermodynamics, you can optimize heating and cooling systems in your home, such as setting thermostats wisely and ensuring proper insulation to minimize energy waste.
How is thermodynamics involved in vehicle operation?
In vehicles, thermodynamics explains how engines convert fuel into motion by transforming chemical energy into thermal energy, and then into mechanical energy, which propels the vehicle.
What everyday examples demonstrate the principles of thermodynamics?
Everyday examples include boiling water, ice melting, and the functioning of heat pumps. These scenarios illustrate concepts like heat transfer, energy conversion, and the laws of thermodynamics in action.