In today’s digital landscape, mastering responsive design is crucial for creating websites that perform well across devices. As you delve deeper, you’ll discover how elements like flexible grids and media queries improve user experience. For those looking to enhance their branding, consider learning how to design dropper bottle labels that adapt seamlessly to various formats.
Understanding Responsive Design
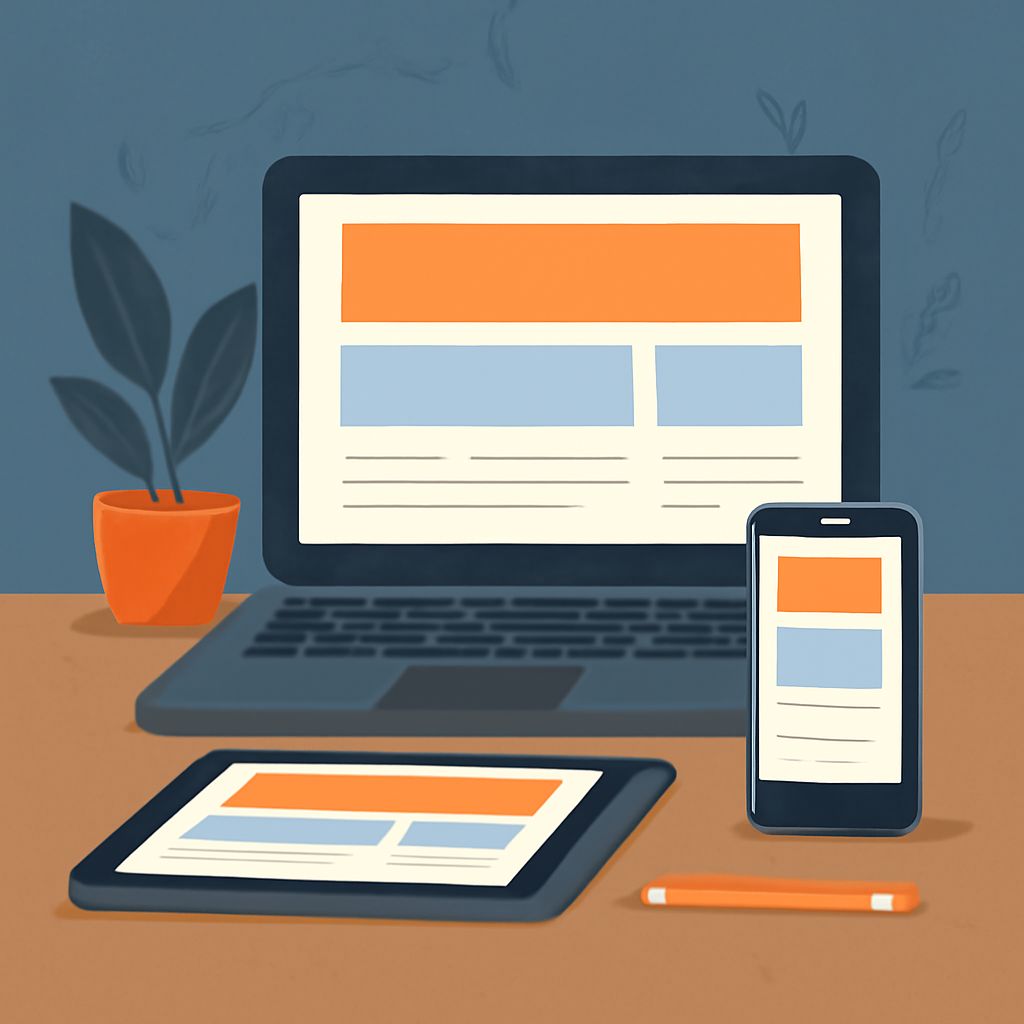
In the ever-evolving world of web development, responsive design stands as a cornerstone of modern website creation. It’s a concept that ensures websites function optimally on various devices and screen sizes. From desktop monitors to mobile phones, a responsive layout adapts seamlessly, providing a consistent user experience.
Responsive design is achieved through a combination of flexible grids, media queries, and scalable images. The goal is to create a fluid and adaptable webpage that maintains usability and aesthetics regardless of the device used to access it.
The Significance of Responsive Design
With the proliferation of smartphones and tablets, internet browsing habits have drastically shifted. As of 2023, mobile devices account for over half of global web traffic. This shift emphasizes the importance of mastering responsive design.
A responsive website enhances user satisfaction, decreases bounce rates, and improves SEO rankings. Search engines like Google prioritize mobile-friendly sites, making responsiveness not just a user-centric feature but also a critical factor in digital marketing strategies.
Benefits of Responsive Design
- Improved User Experience: A responsive site adjusts content and layout to fit the user’s screen, ensuring readability and navigability.
- Increased Reach: By catering to multiple devices, responsive design broadens audience access.
- Cost Efficiency: Maintaining a single website that adapts to various devices is more economical than developing separate versions for each platform.
- SEO Benefits: Google’s algorithm rewards mobile-friendly websites with better search rankings.
Core Components of Responsive Design
Flexible Grids
At the heart of responsive design lies the flexible grid system. Unlike fixed-width layouts, flexible grids use relative units like percentages instead of pixels. This approach enables the layout to adjust dynamically, maintaining coherence as screen sizes vary.
Media Queries
Media queries are a fundamental tool in responsive design. They allow developers to apply different styles based on the device’s characteristics, such as screen width, height, and resolution. This feature helps customize the look and feel of a website, ensuring optimal performance across diverse devices.
| Device | Typical Screen Width | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile | 480px and below | Primary browsing device for many users |
| Tablet | 481px to 768px | Popular for browsing at home or in transit |
| Desktop | 769px and above | Used for intensive tasks and extensive browsing |
Scalable Images and Media
Images and media also need to be flexible. Techniques such as CSS’s max-width property ensure that images adjust to fit their containers, preventing oversized media from disrupting the layout. Additionally, using responsive image tags in HTML5, like the <picture> element, allows serving different images based on device capabilities.
Building a Responsive Layout: Step-by-Step
Step 1: Set Up the Viewport
The viewport meta tag is crucial for responsive design. It instructs browsers on how to control page dimensions and scaling. A typical viewport setting looks like this:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">Step 2: Utilize Fluid Grid Layouts
Instead of traditional grid systems, use CSS Flexbox or Grid to create flexible layouts. These modern layout techniques offer superior control over element alignment and spacing.
Step 3: Implement Media Queries
Implement media queries to apply different styling rules based on device specifications. Here’s a basic example:
@media (max-width: 600px) { body { background-color: lightgreen; } }Step 4: Optimize Images
Ensure images are responsive using CSS rules and HTML5 tags. This approach not only enhances aesthetics but also improves loading times, crucial for mobile users with bandwidth limitations.
Common Challenges in Responsive Design
While responsive design offers numerous benefits, it’s not without challenges. Developers may face issues like:
- Browser Compatibility: Ensuring consistent appearance across various browsers can be daunting.
- Performance Optimization: Responsive sites may become slow if not optimized, particularly on mobile devices.
- Testing and Debugging: Testing across devices and screen sizes is essential but can be time-consuming and complex.
Conclusion
Mastering responsive design is essential for any web developer aiming to create modern, accessible websites. By understanding and implementing the principles of flexible grids, media queries, and scalable media, developers can ensure their websites remain functional and visually appealing on any device. As technology continues to evolve, staying updated with responsive design trends will be key to maintaining a competitive edge in web development.
FAQ
What is a responsive layout?
A responsive layout is a web design approach that ensures a website’s content and elements adjust smoothly across various devices and screen sizes, providing an optimal viewing experience.
Why is responsive design important for beginners?
Responsive design is crucial for beginners because it enhances user experience, improves SEO rankings, and ensures that a website is accessible and functional on all devices, from desktops to mobile phones.
What are the key elements of a responsive layout?
The key elements of a responsive layout include flexible grid systems, scalable images, CSS media queries, and fluid layouts that adapt to different screen sizes.
How do CSS media queries help in responsive design?
CSS media queries enable developers to apply different styles based on device characteristics such as screen width, orientation, and resolution, allowing for tailored layouts for various devices.
What tools can beginners use to test responsive layouts?
Beginners can use tools like Google Chrome’s Developer Tools, Firefox’s Responsive Design Mode, and online services like BrowserStack to test and ensure their layouts are responsive across different devices.
How can beginners start learning responsive layout design?
Beginners can start by studying HTML and CSS basics, exploring frameworks like Bootstrap, practicing with online tutorials, and building simple projects to understand how to implement responsive design techniques effectively.