The integration of polymers in materials science holds substantial promise for creating innovative solutions across various industries. As we explore these advancements, the potential for sustainable practices, such as eco-friendly bag designs, becomes increasingly relevant, showcasing how modern materials can meet both functional and environmental needs.
Polymers have become integral to the advancement of materials science, revolutionizing industries and enhancing everyday products. From the plastic containers we use daily to the high-performance materials in aerospace and medical applications, polymers are versatile materials that offer unique properties. This article delves into how polymers are transforming materials science, exploring their properties, applications, and the future of polymer technology.
The Basics of Polymers
Polymers are large molecules composed of repeating structural units called monomers. These monomers are linked together through chemical bonds, creating chains that can vary in length and complexity. Polymers can be categorized based on their origin and structure:
- Natural Polymers: Found in nature, these include proteins, cellulose, and rubber.
- Synthetic Polymers: Man-made materials such as polyethylene, nylon, and polystyrene.
- Thermoplastics: These can be melted and reshaped multiple times without significant degradation.
- Thermosetting Polymers: These harden permanently after being shaped, offering high thermal stability.
Properties That Define Polymers
The unique properties of polymers are what make them so valuable in materials science. Here are some of the key characteristics:
Mechanical Properties
Polymers exhibit a range of mechanical properties that can be tailored for specific applications:
- Elasticity: Polymers can stretch and return to their original shape, which is crucial for applications like rubber bands.
- Tensile Strength: Some polymers possess high strength, making them suitable for structural applications.
- Ductility: Many polymers can be drawn into thin films or fibers without breaking.
Thermal Properties
The ability of polymers to withstand heat is vital in many industries:
| Property | Thermoplastics | Thermosets |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | Reversible processing | Fixed structure |
| Thermal Conductivity | Generally low | Varies widely |
| Heat Resistance | Lower than thermosets | High heat resistance |
Chemical Resistance
Polymers’ resistance to chemicals can make them ideal for containers and pipes:
- Hydrophobic Polymers: Repel water and many solvents.
- Biodegradable Polymers: Designed to decompose under specific conditions.
- Corrosion-Resistant Polymers: Suitable for aggressive environments, particularly in industrial applications.
Applications of Polymers in Modern Science
Polymers have myriad applications across various sectors:
Aerospace and Automotive Industries
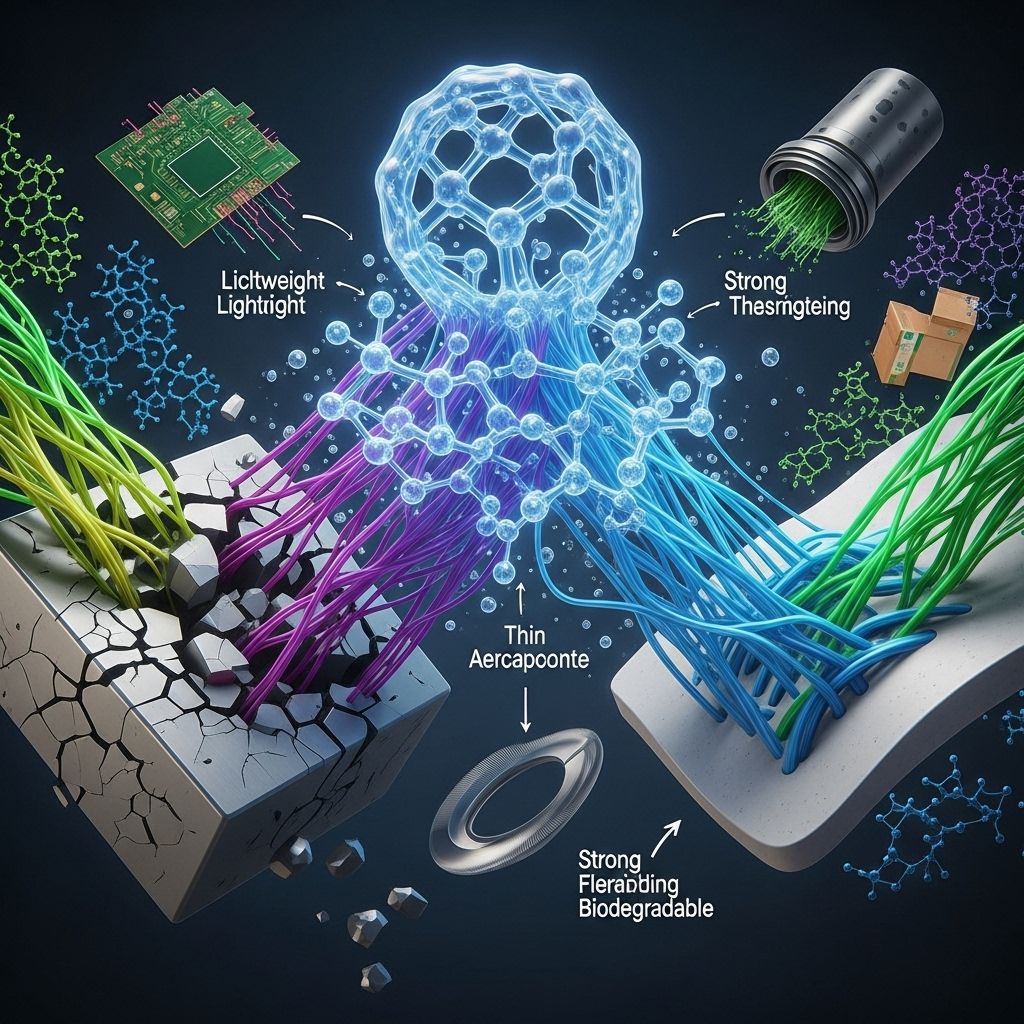
In aerospace and automotive engineering, weight reduction is critical for fuel efficiency. Polymers are used in:
- Lightweight composite materials for fuselage and wings.
- Interior components that reduce overall vehicle weight.
- Flame-retardant coatings that enhance safety.
Medical Applications
Polymers are essential in the field of medicine, where they serve diverse roles:
- Biocompatible Devices: Used in stents, catheters, and artificial organs.
- Drug Delivery Systems: Polymers can encapsulate drugs for controlled release.
- Wound Dressings: Advanced polymers provide moisture control and promote healing.
Electronics and Energy Storage
Polymers are also making significant strides in electronics:
- Conductive polymers are used in flexible electronics.
- Polymer batteries provide lightweight and efficient energy storage solutions.
- Organic solar cells utilize polymer-based materials for energy conversion.
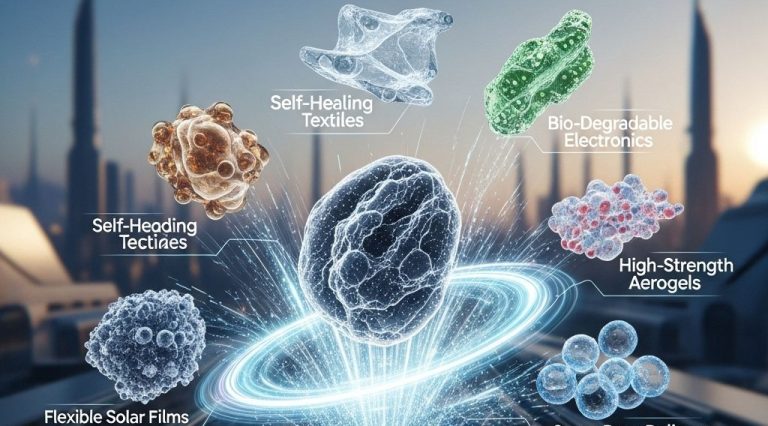
The Future of Polymer Research
As we look to the future, polymer science is set to expand even further. Research trends include:
Nanotechnology
Incorporating nanoparticles into polymer matrices can enhance properties:
- Improved mechanical strength
- Enhanced thermal stability
- Increased chemical resistance
Smart Polymers
These materials can respond to environmental stimuli, such as:
- Temperature: Altering properties based on heat.
- pH Levels: Changing structure in response to acidity.
- Light: Polymers that can change color or shape when exposed to light.
Recycling and Sustainability
With growing environmental concerns, the development of sustainable polymers is crucial:
- Biodegradable plastics that reduce landfill waste.
- Recyclable polymers that can be repurposed for new products.
- Renewable feedstocks that minimize reliance on fossil fuels.
Conclusion
The transformative effect of polymers in materials science is evident across multiple industries. Their unique properties and adaptability continue to drive innovation, offering solutions to some of modern society’s most pressing challenges. As we advance into a future shaped by sustainability and smart technology, the role of polymers will undoubtedly expand, cementing their status as key materials in both industrial and everyday applications.
FAQ
What are polymers and how do they function in materials science?
Polymers are large molecules made up of repeating structural units called monomers. They play a crucial role in materials science by providing unique properties such as flexibility, durability, and resistance to chemicals, which can be tailored for specific applications.
How are polymers used in everyday products?
Polymers are used in a wide variety of everyday products including plastics, rubber, fibers, and even medical devices. Their versatility allows them to be molded into different shapes and forms to meet diverse consumer needs.
What advancements have been made in polymer technology?
Recent advancements in polymer technology include the development of bio-based and biodegradable polymers, smart polymers that respond to environmental changes, and nanocomposites that enhance material strength and functionality.
How do polymers contribute to sustainability in materials science?
Polymers contribute to sustainability by enabling the creation of lightweight, energy-efficient materials and by promoting the use of biodegradable alternatives which reduce plastic waste and environmental impact.
What role do polymers play in the field of medicine?
In medicine, polymers are used in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, and biocompatible implants. They can be engineered to interact with biological systems, improving patient outcomes and treatment efficacy.
What future trends can we expect in polymer science?
Future trends in polymer science include the development of self-healing materials, advanced composites, and the integration of polymer technology with nanotechnology to create smarter, more efficient materials.