Understanding photosynthesis is essential for appreciating how plants thrive and sustain ecosystems. By learning about this natural process, you can gain insights into environmental balance and energy flow. For creatives involved in design projects, exploring tools like designer bag templates can help in visually representing such concepts.
Photosynthesis is one of nature’s most fascinating processes, enabling plants to convert sunlight into energy. This complex mechanism not only sustains plant life but also supports the entire ecosystem, including humans. Understanding photosynthesis can reveal a lot about how life on Earth functions and how we can better appreciate the intricate balance of nature.
What is Photosynthesis?
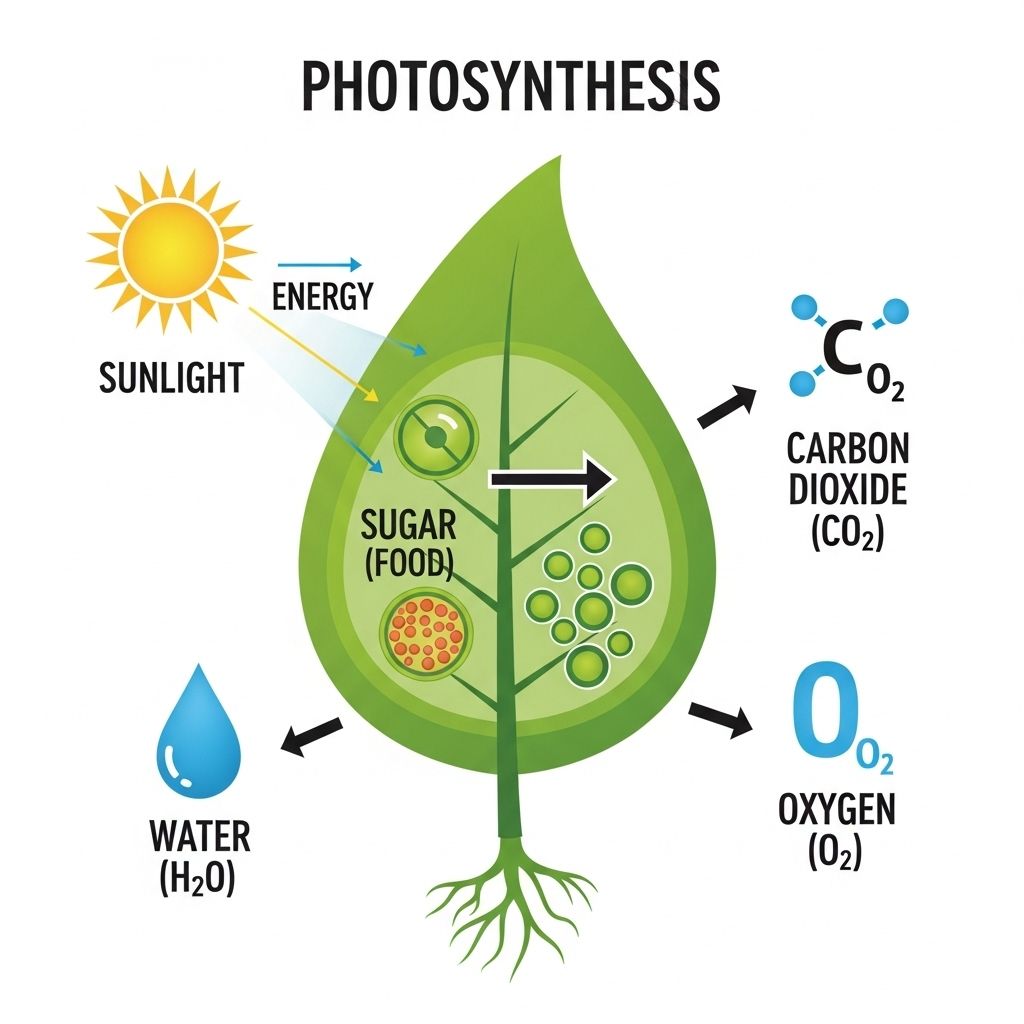
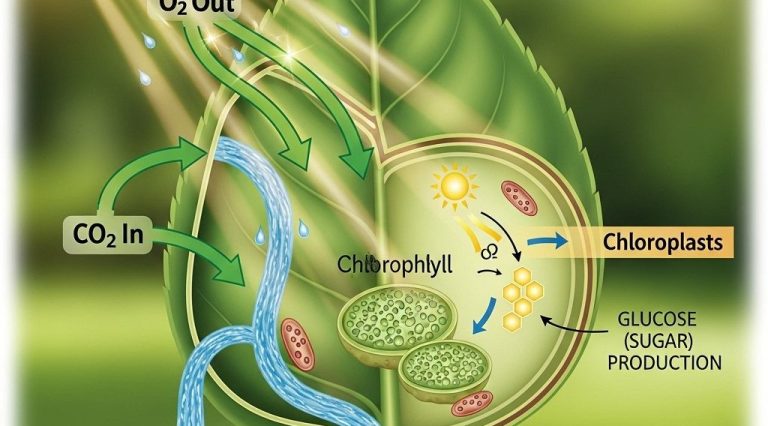
At its core, photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy. This process primarily occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells, where chlorophyll, the green pigment, plays a crucial role. Through a series of reactions, organisms transform carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, which are essential for life.
The Key Components of Photosynthesis
1. Light Energy
Light energy, primarily from the sun, is the driving force behind photosynthesis. Plants capture this energy using their leaves, which are adapted to absorb sunlight efficiently.
2. Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is the pigment responsible for the green color of plants. It absorbs light most effectively in the blue and red wavelengths while reflecting green light, which is why plants appear green.
3. Water
Water is a vital component in the photosynthesis process and is absorbed by plant roots from the soil. It acts as a reagent in the chemical reactions that convert light energy into glucose.
4. Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is taken from the atmosphere through small openings in leaves called stomata. Plants utilize this gas during the photosynthesis process to produce glucose.
The Photosynthesis Process Explained
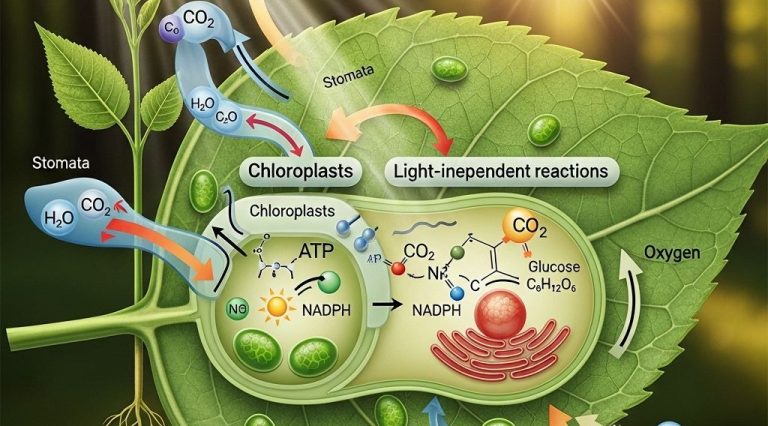
The process of photosynthesis can be broken down into two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle).
Stage 1: Light-Dependent Reactions
This stage occurs in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts and requires sunlight. Here’s how it works:
- **Photons from sunlight are absorbed** by chlorophyll.
- **Water molecules are split**, releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
- **Energy from the light** is converted into chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH.
Stage 2: Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
This stage occurs in the stroma of the chloroplasts and does not directly require light. It uses the chemical energy produced in the first stage to convert carbon dioxide into glucose through a series of reactions:
- **Carbon dioxide is fixed** into a 5-carbon sugar (ribulose bisphosphate).
- **ATP and NADPH** are used to convert the fixed carbon into glucose.
- **Glucose is synthesized**, which can be used for energy or stored as starch.
Importance of Photosynthesis
1. Primary Source of Energy
Photosynthesis is the foundation of the food chain. Plants are primary producers, meaning they produce energy that is consumed by herbivores, which in turn are eaten by carnivores.
2. Oxygen Production
As a byproduct of photosynthesis, oxygen is released into the atmosphere, which is essential for the survival of aerobic organisms, including humans.
3. Carbon Dioxide Regulation
Photosynthesis plays a crucial role in regulating atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, helping to mitigate climate change by converting CO2 into organic compounds.
Photosynthesis in Different Organisms
While photosynthesis is most commonly associated with plants, it also occurs in various organisms:
1. Algae
Algae, found in both freshwater and marine environments, perform photosynthesis much like plants. They are significant contributors to global oxygen production.
2. Cyanobacteria
These bacteria, sometimes referred to as blue-green algae, are among the oldest organisms on Earth and perform a form of photosynthesis similar to plants.
3. Photosynthetic Protists
Some single-celled organisms, such as Euglena, can photosynthesize, showcasing the diversity of life forms that utilize this process.
Challenges Facing Photosynthesis
Despite its importance, photosynthesis faces several challenges:
1. Climate Change
Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns may disrupt photosynthesis, affecting plant growth and productivity.
2. Pollution
Air and water pollution can hinder the photosynthesis process by damaging plant tissues or changing the composition of essential resources like water and CO2.
3. Deforestation
The loss of forests decreases the number of photosynthetic organisms, negatively impacting oxygen production and carbon sequestration.
Innovations and Future of Photosynthesis Research
Scientists are exploring ways to enhance photosynthesis to improve crop yields and combat climate change:
1. Genetic Engineering
By modifying the genetic makeup of plants, researchers aim to create species that can photosynthesize more efficiently and withstand environmental stressors.
2. Artificial Photosynthesis
Scientists are developing systems that mimic natural photosynthesis to produce clean fuels and reduce atmospheric CO2 levels.
3. Sustainable Practices
Implementing sustainable agricultural practices can enhance the efficiency of photosynthesis, ensuring food security and promoting environmental health.
Conclusion
Photosynthesis is a remarkable process that sustains life on Earth. By understanding its mechanisms and importance, we can better appreciate the delicate balance of our ecosystem and work towards preserving it for future generations. As we continue to innovate and seek solutions to contemporary challenges, harnessing the power of photosynthesis may be key to a sustainable future.
FAQ
What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight into energy, using carbon dioxide and water.
How do plants perform photosynthesis?
Plants perform photosynthesis using chlorophyll in their leaves, which captures sunlight and helps convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
What are the main products of photosynthesis?
The main products of photosynthesis are glucose, which plants use for energy, and oxygen, which is released into the atmosphere.
Why is photosynthesis important?
Photosynthesis is important because it provides oxygen for us to breathe and is the foundation of the food chain, as it produces energy for plants and, consequently, for animals.
What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis?
The rate of photosynthesis can be affected by light intensity, carbon dioxide levels, temperature, and the availability of water.