In the journey of mastering the concepts of acids and bases, one might draw parallels to the pursuit of sustainability in various fields, including design. Just as understanding these fundamental chemical properties is vital in science, integrating principles like eco-friendly bag designs showcases the importance of environmentally conscious choices in modern product development.
In the ever-evolving landscape of science, understanding the foundational concepts of acids and bases remains crucial. As we move deeper into 2025, the importance of acids and bases transcends beyond traditional chemistry classrooms, permeating into fields like biotechnology, environmental science, and even digital technologies. This article explores the fundamental properties of acids and bases, their applications in modern science, and the innovative research that continues to reshape our understanding of these chemical entities.
The Basics of Acids and Bases
At their core, acids and bases are defined by their unique properties and the reactions they undergo. The Bronsted-Lowry theory, which classifies acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors, is one of the most widely accepted definitions. Let’s take a closer look at the characteristics that define these two groups:
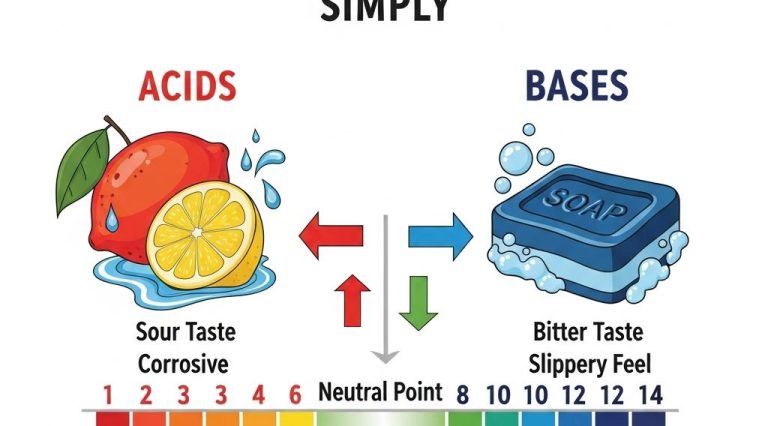
Characteristics of Acids
- They have a sour taste (e.g., citric acid in lemons).
- They turn blue litmus paper red.
- They react with metals to produce hydrogen gas.
- They neutralize bases.
Characteristics of Bases
- They have a bitter taste and slippery feel (e.g., soap).
- They turn red litmus paper blue.
- They react with acids to form salts and water.
- They can cause chemical burns.
The pH Scale: Measuring Acidity and Basicity
The pH scale is a vital tool in chemistry used to measure the acidity or basicity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Understanding the pH scale is essential for many scientific applications. Here’s how it breaks down:
| pH Value | Nature |
|---|---|
| 0-6.9 | Acidic |
| 7 | Neutral |
| 7.1-14 | Basic |
Measuring pH can be done using various methods, including:
- pH Indicators (like litmus paper)
- pH Meters for precise measurements
- Natural Indicators (like red cabbage juice)
Applications of Acids and Bases in Modern Science
In 2025, the applications of acids and bases are more profound and varied than ever. Here are some key areas where their roles are particularly significant:
Biotechnology
In biotechnology, the manipulation of pH plays a crucial role in various processes:
- Fermentation: Many fermentation processes depend on maintaining optimal pH levels to encourage bacterial growth.
- Enzyme Activity: Most enzymes have a specific pH range in which they function best, making pH control a vital aspect of biochemical manufacturing.
Environmental Science
Acids and bases significantly impact environmental chemistry, influencing everything from soil quality to water ecosystems. Key considerations include:
- Acid Rain: Resulting from industrial emissions, acid rain can alter soil pH, affecting plant life.
- Soil Amendment: Farmers often adjust soil pH using lime (a base) or sulfur (an acid) to improve crop yields.
Pharmaceuticals
The pharmaceutical industry relies heavily on acids and bases for drug development and formulation. Considerations involve:
- Drug Stability: The pH of drug formulations can affect stability and solubility.
- Absorption Rates: The acidic or basic nature of a drug can influence its absorption in the human body.
Innovative Research and Future Directions
Looking ahead, research into acids and bases continues to push the boundaries of science. Some exciting avenues include:
Green Chemistry
Green chemistry focuses on designing chemical processes and products that minimize environmental impact. In this context, the use of benign acids and bases as catalysts is gaining traction:
- Biodegradable acids derived from natural sources are being explored as alternatives to synthetic acids.
- Using waste products as bases in chemical reactions to exemplify sustainability.
Nanomaterials
Research into nanomaterials also demonstrates the application of acid-base chemistry:
- Nanoparticle Synthesis: The synthesis of nanoparticles often involves acid-base reactions to control particle size and morphology.
- Environmental Remediation: Nanomaterials can help remove pollutants, with their effectiveness often reliant on their acidic or basic properties.
Conclusion
As we traverse through 2025, the understanding of acids and bases remains pivotal across various scientific disciplines. Their unique properties, measurement techniques, and applications in biotechnology, environmental science, and pharmaceuticals highlight their enduring relevance. Furthermore, ongoing research into green chemistry and nanomaterials promises to unveil new opportunities for harnessing these fundamental chemical entities. As we embrace future innovations, a solid grasp of acids and bases will undoubtedly remain a cornerstone of scientific advancement.
FAQ
What are acids and bases?
Acids are substances that donate protons (H+) in a chemical reaction, while bases accept protons. They play crucial roles in various chemical processes and everyday life.
How do acids and bases affect pH levels?
Acids lower the pH of a solution, making it more acidic, while bases raise the pH, making it more alkaline. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral.
What are some common examples of acids and bases?
Common acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl) found in stomach acid and citric acid in fruits. Common bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH) used in drain cleaners and baking soda (sodium bicarbonate).
What is the significance of the acid-base balance in the human body?
Maintaining acid-base balance is essential for proper cellular function. The body regulates pH levels through various mechanisms, including respiration and kidney function.
How can I safely handle acids and bases?
Always wear protective gear such as gloves and goggles when handling acids and bases. Ensure proper ventilation and follow safety guidelines to prevent accidents.
What are some practical applications of acids and bases in daily life?
Acids and bases are used in cleaning products, food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and even in the manufacturing of various goods, highlighting their importance in our daily lives.