As you embark on your journey to master electrical circuits, it’s essential to grasp the core concepts that underpin this fascinating field. Understanding how circuits work can enhance your practical skills and pave the way for innovative projects. For those looking to elevate their ideas, consider exploring promotional bag ideas that can help you showcase your creativity in producing visual aids for your electrical circuit concepts.
Understanding electrical circuits is essential for anyone engaged in the field of electronics or electrical engineering. Whether you’re a beginner or seeking to brush up on your skills, grasping the fundamentals can open up new avenues in your technological journey. This article will break down the crucial components of electrical circuits and explain how they work together to form a complete system.
What is an Electrical Circuit?
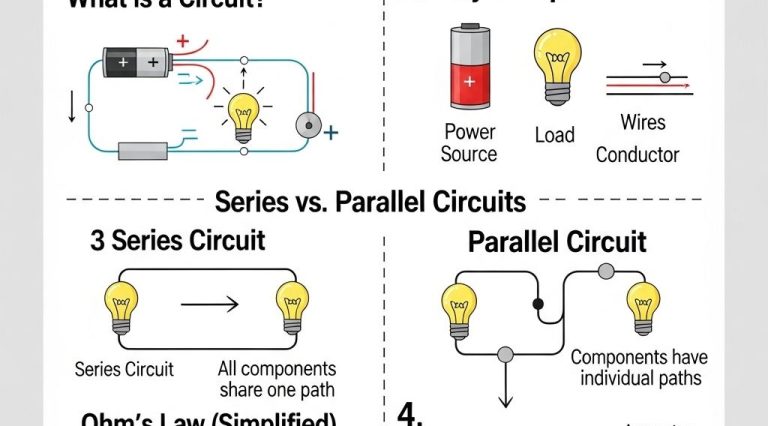
An electrical circuit is a path that allows electric current to flow, enabling devices to function. The basic structure of a circuit consists of several key components that facilitate this flow:
- Power Source: Provides the voltage to push the current through the circuit (e.g., batteries, power supplies).
- Conductors: Typically made from copper or aluminum, these wires connect various components and provide a pathway for current.
- Load: Any device that consumes electrical energy (e.g., light bulbs, motors).
- Switch: Allows for the control of current flow in the circuit.
Types of Circuits
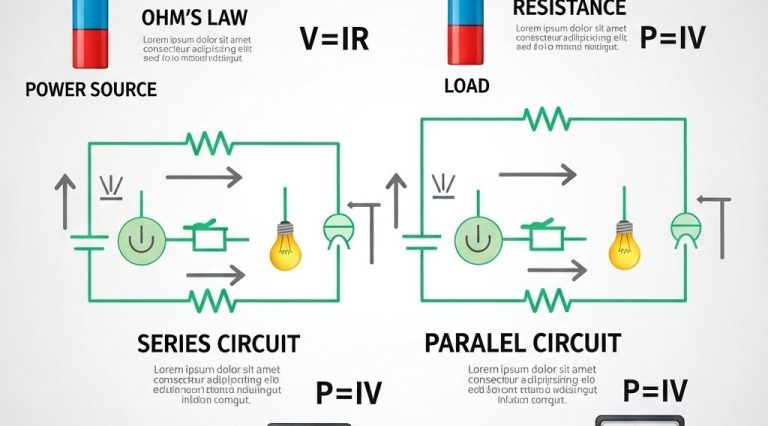
Series Circuits
In a series circuit, components are connected end-to-end, forming a single path for the current to flow. If one component fails, the entire circuit is interrupted.
Parallel Circuits
Parallel circuits provide multiple paths for current to flow. If one component fails, the current can still pass through other paths, allowing other components to function.
Comparison Table: Series vs. Parallel Circuits
| Feature | Series Circuit | Parallel Circuit |
|---|---|---|
| Current Flow | Same through all components | Divided among branches |
| Voltage | Divided among components | Same across all branches |
| Failure | Entire circuit fails if one component fails | Can continue functioning if one branch fails |
Basic Circuit Components
1. Resistors
Resistors are components that limit the flow of electric current. They are measured in ohms (Ω) and come in various forms:
- Fixed Resistors: Have a specific resistance value.
- Variable Resistors (Potentiometers): Allow for adjustable resistance.
2. Capacitors
Capacitors store and release electrical energy in a circuit. They are used in applications like filtering, timing, and energy storage.
3. Inductors
Inductors store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them. They are commonly used in filters and transformers.
4. Diodes
Diodes allow current to flow in one direction only, making them crucial for converting AC to DC current.
Understanding Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law is fundamental in circuit theory and relates voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) with the formula:
V = I × R
Practical Applications of Ohm’s Law
Using Ohm’s Law, you can calculate:
- Voltage drops across components.
- Current flowing through the circuit.
- Resistance needed to achieve desired current levels.
Using Multimeters in Circuit Testing
A multimeter is an essential tool for measuring voltage, current, and resistance. Here are some basic steps to using a multimeter:
Step-by-Step Guide
- Set the multimeter to the desired measurement type (voltage, current, resistance).
- Connect the probes to the circuit: red to positive and black to negative.
- Read the measurement displayed on the screen.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical circuits can be dangerous. Here are some safety tips to ensure your well-being:
- Always disconnect power before working on circuits.
- Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shock.
- Be aware of your surroundings and avoid working in wet conditions.
Conclusion
With a basic understanding of electrical circuits and their components, you can embark on various projects, from simple circuits to more complex systems. Whether you aim to build, troubleshoot, or innovate, mastering the essentials of electrical circuits is a valuable skill. The world of electronics is vast and ever-evolving, and having a solid foundation will empower you to explore and implement new technologies with confidence.
FAQ
What is an electrical circuit?
An electrical circuit is a closed loop that allows electric current to flow, consisting of a power source, conductors, and a load.
What are the main components of an electrical circuit?
The main components of an electrical circuit include the power source (like a battery), conductors (wires), and loads (devices that use electricity, like bulbs or motors).
What is the difference between series and parallel circuits?
In a series circuit, components are connected one after the other, while in a parallel circuit, components are connected across common points, allowing multiple paths for current.
How does current flow in a circuit?
Current flows from the positive terminal of the power source, through the circuit, and returns to the negative terminal, driven by voltage.
What is Ohm’s Law?
Ohm’s Law states that the current flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance.
What safety precautions should be taken when working with electrical circuits?
When working with electrical circuits, always disconnect power before handling wires, use insulated tools, and ensure proper grounding to avoid electrical shock.