Marine biology offers insights into the diverse ecosystems of our oceans, making it essential for understanding our planet’s health. As you delve into key concepts in this field, you might also find it interesting to explore related creative projects, such as designer bag templates, which can help visualize marine themes in unique ways.
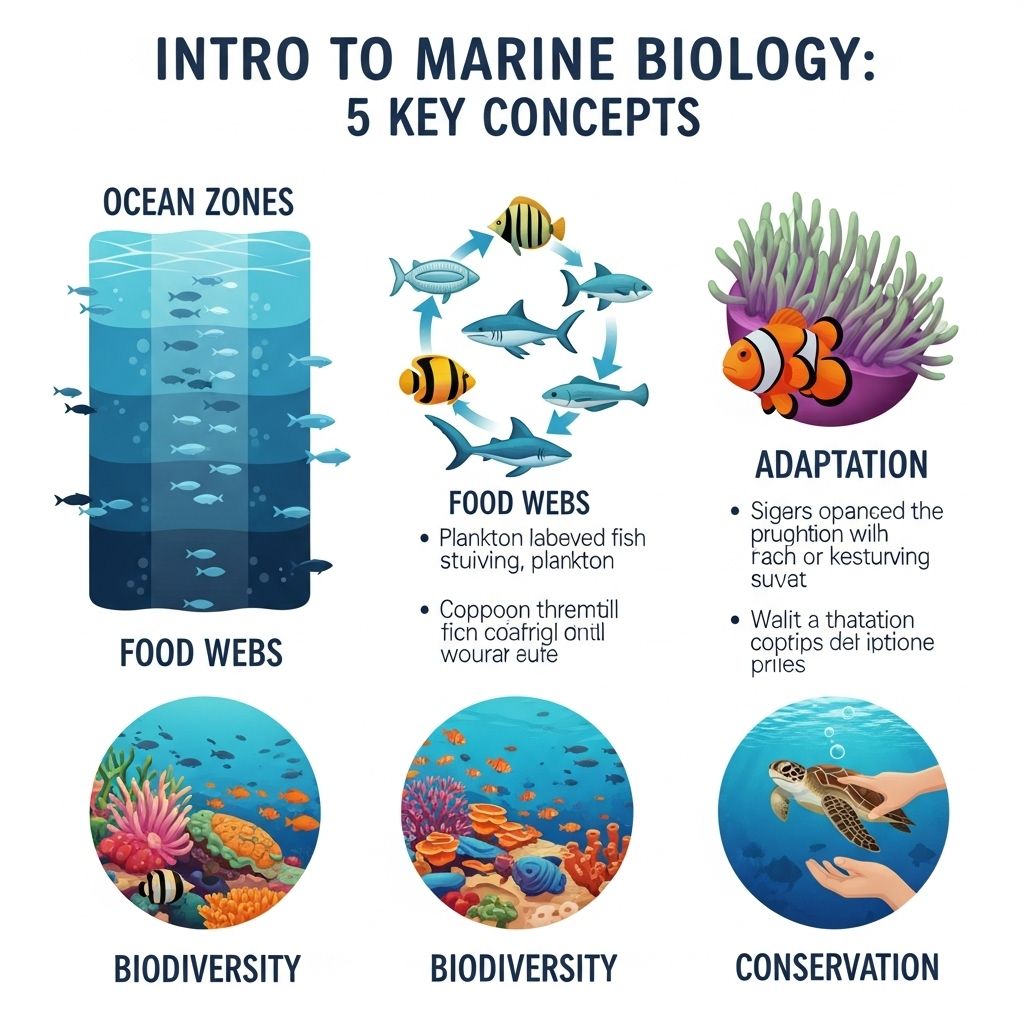
Marine biology is a dynamic and fascinating field that explores the diverse life forms inhabiting our oceans and the intricate ecosystems that support them. This science delves into the interactions between marine organisms and their environments, examining everything from microscopic plankton to the largest mammals on Earth. In this article, we will explore five key concepts that form the foundation of marine biology, providing insight into the complexity of oceanic life.
The Importance of Marine Ecosystems
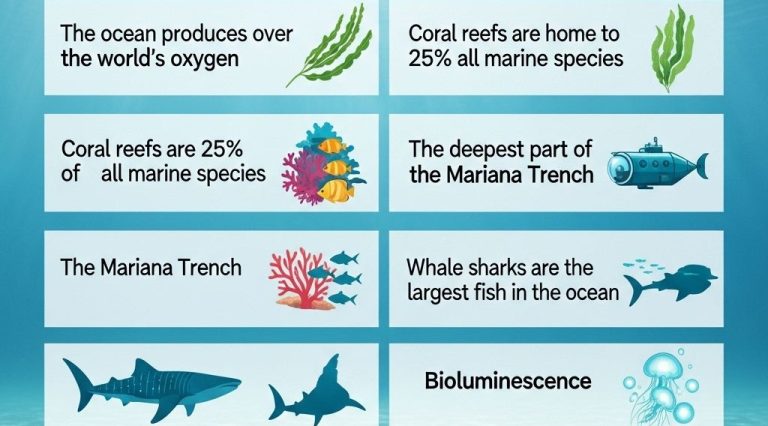
Marine ecosystems cover over 70% of the Earth’s surface and play a critical role in supporting life on our planet. They are essential for a multitude of reasons:
- Oxygen Production: Phytoplankton, tiny marine plants, contribute more than 50% of the Earth’s oxygen through photosynthesis.
- Climate Regulation: Oceans absorb carbon dioxide and heat, helping to mitigate climate change.
- Habitats: Marine environments provide habitat for a vast array of organisms, from microscopic bacteria to gigantic whales.
- Food Security: The ocean is a primary source of food for billions of people worldwide.
- Economic Value: Marine resources contribute significantly to economies through fisheries, tourism, and recreation.
Diversity of Marine Life
The sheer diversity of marine life is one of the most captivating aspects of marine biology. Organisms in the ocean can be categorized into various groups:
Plankton
These are organisms that drift with ocean currents and include:
- Phytoplankton: Microscopic plants that form the base of the marine food web.
- Zooplankton: Small animals that feed on phytoplankton and other zooplankton.
nekton
Nekton consists of actively swimming organisms, such as:
- Fish: They are the most diverse group of vertebrates in the ocean.
- Mammals: Includes whales, dolphins, and seals.
- Cephalopods: Octopuses, squids, and cuttlefish known for their intelligence.
Benthos
Benthos are organisms that live on or near the ocean floor, including:
- Crustaceans: Crabs, lobsters, and shrimp.
- Mollusks: Oysters, clams, and snails.
- Echinoderms: Starfish and sea urchins.
Adaptations to Marine Environments
Marine organisms have developed a variety of adaptations to survive and thrive in their environments. These adaptations can be classified into different categories:
Physical Adaptations
Many marine species possess physical traits to enhance their survival, such as:
- Streamlined Bodies: Fish and marine mammals have streamlined shapes to reduce drag.
- Coloration: Camouflage and bioluminescence help organisms avoid predators or attract prey.
Behavioral Adaptations
Behavioral strategies also play a vital role:
- Migration: Many species, such as salmon, migrate to reproduce.
- Social Structures: Some animals, like dolphins, form complex social groups for cooperative hunting.
Threats to Marine Life
Despite the resilience of marine ecosystems, they face numerous threats, largely due to human activities. Key threats include:
Pollution
Marine pollution comes from various sources, including:
- Plastic Waste: Millions of tons of plastic enter the oceans annually, harming marine life.
- Chemical Runoff: Fertilizers and pesticides contribute to nutrient pollution, leading to harmful algal blooms.
Climate Change
Climate change significantly impacts marine environments through:
- Ocean Acidification: Increased CO2 levels lower the pH of seawater, affecting organisms like coral and shellfish.
- Warming Oceans: Changes in temperature disrupt marine ecosystems and species distributions.
Conservation Efforts in Marine Biology
Conserving marine ecosystems is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and supporting human life. Various strategies are being implemented to protect these vital resources:
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs)
MPAs are regions where human activity is restricted to protect the marine environment:
- They help preserve biodiversity.
- Support fish populations recovery.
- Enhance ecosystem resilience against climate change.
Restoration Initiatives
Efforts are being made to restore damaged marine environments:
- Coral Reef Restoration: Techniques like coral gardening are being used to rehabilitate degraded reefs.
- Seagrass and Mangrove Restoration: Replanting efforts are crucial for carbon sequestration and habitat provision.
The Future of Marine Biology
The future of marine biology is both exciting and challenging. With advancements in technology, researchers have new tools for exploration and conservation efforts:
Technological Innovations
Emerging technologies such as:
- Remote Sensing: Helps monitor ocean health and changes in ecosystems.
- Underwater Robotics: Allows for deep-sea exploration and data collection in hard-to-reach areas.
Citizen Science
Engaging the public in scientific research can enhance data collection:
- Beach Cleanups: Community efforts can reduce pollution.
- Species Monitoring: Public participation in tracking species helps build extensive databases.
In conclusion, marine biology provides a glimpse into the wondrous diversity of life beneath the waves and highlights the importance of ocean conservation. As we deepen our understanding of marine ecosystems, we can foster greater stewardship of our oceans and ensure their health for generations to come.
FAQ
What are the fundamental concepts of marine biology?
The fundamental concepts of marine biology include marine ecosystems, biodiversity, oceanography, marine organisms, and conservation.
Why is biodiversity important in marine biology?
Biodiversity is crucial in marine biology as it enhances ecosystem resilience, supports food webs, and provides resources for human use and pharmaceuticals.
How do oceanographic processes affect marine life?
Oceanographic processes, such as currents, temperature, and salinity, influence nutrient distribution, habitat availability, and the overall health of marine ecosystems.
What types of organisms are studied in marine biology?
Marine biology studies a diverse range of organisms, including plankton, fish, marine mammals, corals, and seaweeds.
What role does conservation play in marine biology?
Conservation is vital in marine biology to protect marine habitats, manage fisheries sustainably, and mitigate the impacts of climate change on ocean life.