In the world of cybersecurity, understanding encryption is crucial for protecting sensitive data. Just as different industries choose bag mockups to showcase their products, organizations must select the right encryption methods to secure their information. This article examines the principles of encryption and its vital role in maintaining data integrity and user privacy.
In today’s digital age, the protection of sensitive information has become paramount. With the rise of cyber threats and data breaches, encryption has emerged as a key component in safeguarding data integrity and privacy. This article delves into the intricacies of encryption, exploring its mechanisms, types, and applications in the realm of cybersecurity.
Understanding Encryption
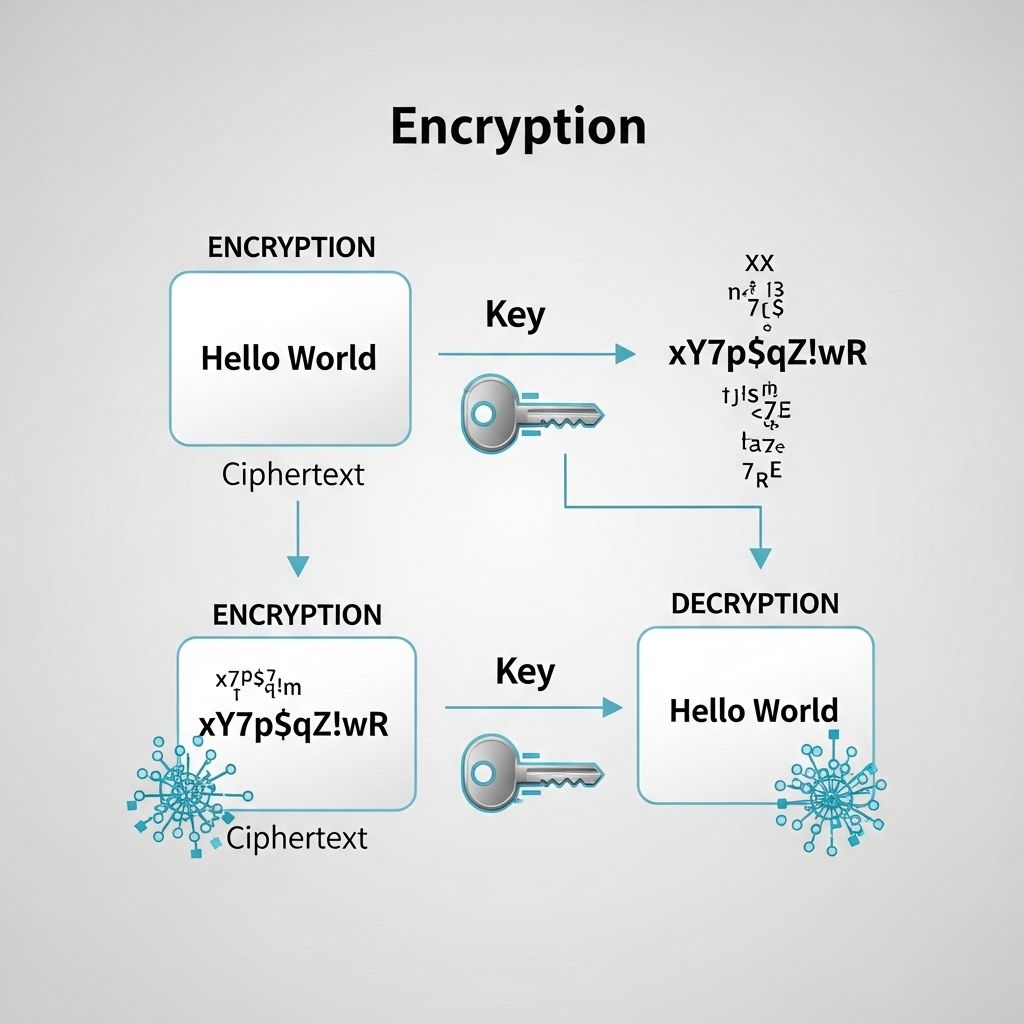
Encryption is the process of converting information or data into a code, especially to prevent unauthorized access. It ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the correct decryption key. The principle of encryption is simple: transform plain text into cipher text that can only be deciphered by someone possessing the appropriate key.
The Importance of Encryption
Encryption plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive information across various sectors. Its significance can be summarized as follows:
- Data Protection: Keeps sensitive data safe from unauthorized access.
- Privacy Assurance: Helps maintain user privacy by safeguarding personal information.
- Compliance: Many industries are required to comply with regulations that mandate encryption of sensitive data.
- Trust Building: Organizations that prioritize data security foster trust among users and clients.
Types of Encryption
Encryption can be broadly classified into two categories: symmetric and asymmetric encryption. Understanding the differences between these types is essential for implementing effective security measures.
Symmetric Encryption
In symmetric encryption, the same key is used for both encryption and decryption. This means that both the sender and recipient must securely share the key beforehand. Key characteristics include:
- Speed: Symmetric encryption is generally faster than asymmetric encryption.
- Key Management: Secure key management is critical because the same key must be kept secret.
- Common Algorithms: Examples include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), DES (Data Encryption Standard), and Blowfish.
Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key cryptography, utilizes a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This method enhances security but comes with a performance trade-off. Key aspects include:
- Public and Private Keys: The public key can be shared openly, while the private key must remain confidential.
- Security: Provides a higher level of security and addresses key distribution issues.
- Common Algorithms: RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm), and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography).
How Encryption Works
The encryption process involves several steps, which can vary based on the encryption method used. Below is a simplified overview of how both symmetric and asymmetric encryption work.
Symmetric Encryption Process
- Key Generation: A secret key is generated.
- Data Input: The data to be encrypted (plain text) is prepared.
- Encryption: The algorithm uses the key to transform the plain text into cipher text.
- Data Transfer: The cipher text is sent to the recipient.
- Decryption: The recipient uses the same key to convert the cipher text back into plain text.
Asymmetric Encryption Process
- Key Pair Generation: A public and private key pair is generated.
- Public Key Distribution: The public key is shared with anyone needing to send encrypted data.
- Encryption: The sender encrypts the data using the recipient’s public key.
- Data Transfer: The encrypted data (cipher text) is sent.
- Decryption: The recipient uses their private key to decrypt the cipher text back into plain text.
Applications of Encryption
Encryption is applied in various fields to enhance security and protect sensitive information. Here are some notable applications:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Secure Communication | Encryption secures communications via email and messaging apps. |
| Data Storage | Protects sensitive data stored on devices and cloud services. |
| Financial Transactions | Encrypts data transmitted during online transactions to prevent fraud. |
| VPNs | Virtual Private Networks use encryption to secure internet connections. |
| Digital Signatures | Authenticates the identity of senders in digital communications. |
Challenges in Encryption
While encryption is a powerful tool, there are challenges and limitations that organizations must navigate:
Key Management
Managing encryption keys securely is critical, as losing a key can result in data being irretrievable. Strategies for effective key management include:
- Regularly rotating keys.
- Using hardware security modules (HSMs).
- Implementing strict access controls.
Performance Overheads
Encryption can cause latency in data processing and transmission. Organizations need to balance security needs with performance requirements.
Regulatory Compliance
Organizations must navigate complex regulations regarding encryption usage in their industry. Understanding these requirements is crucial for compliance.
The Future of Encryption
As technology evolves, so do the methods and practices surrounding encryption. Emerging trends that could shape the future of encryption include:
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computers pose potential threats to traditional encryption methods, necessitating the development of quantum-resistant algorithms.
- Homomorphic Encryption: This allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without needing to decrypt it first, enhancing data privacy and security.
- Increased Regulation: As data breaches continue to rise, governments may impose stricter regulations around encryption standards.
Conclusion
Encryption is a fundamental aspect of cybersecurity that protects sensitive information from unauthorized access. By understanding its mechanisms, types, and applications, organizations can better implement effective security measures to safeguard their data. As technology continues to advance, staying informed about encryption practices will be essential in combating evolving cyber threats.
FAQ
What is encryption in cybersecurity?
Encryption is the process of converting data into a coded format to prevent unauthorized access, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential.
How does encryption protect my data?
Encryption protects data by transforming it into an unreadable format for anyone who does not possess the appropriate decryption key, thereby safeguarding it from cyber threats.
What are the different types of encryption methods?
The main types of encryption methods include symmetric encryption, where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption, and asymmetric encryption, which uses a pair of keys—a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
Why is encryption important for online communications?
Encryption is vital for online communications as it secures sensitive information, such as personal data and financial transactions, from being intercepted by cybercriminals during transmission.
Can encryption prevent all cyber attacks?
While encryption significantly enhances data security, it cannot prevent all cyber attacks. It is a crucial part of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that should also include other measures like firewalls and antivirus software.
How can I implement encryption for my business?
Businesses can implement encryption by utilizing encryption software, securing emails, using virtual private networks (VPNs), and ensuring that sensitive data stored on servers or devices is encrypted.