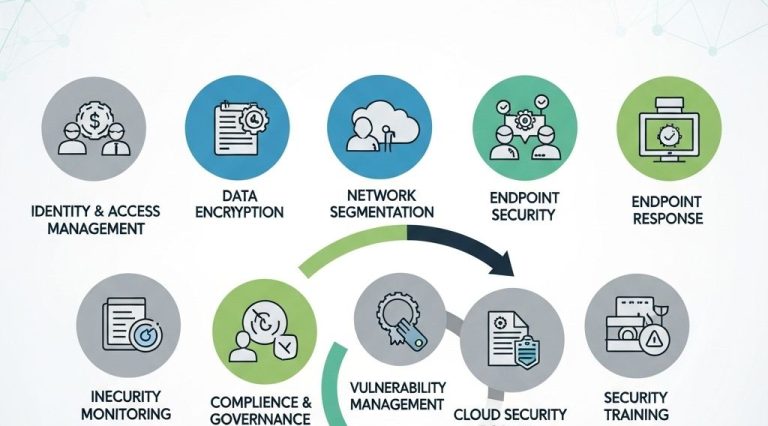
As agile teams embrace cloud-native architectures, they must also navigate the associated security challenges. This involves integrating security practices throughout the development lifecycle to protect applications and data effectively. For teams looking to enhance their branding and development process, utilizing mockup templates for bags can help in visualizing product designs while maintaining security protocols.
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, agile teams are increasingly adopting cloud-native architectures to enhance flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. However, with these advancements come new security challenges. Protecting applications and data in a cloud-native environment requires a nuanced approach, integrating security throughout the development lifecycle. This article explores essential strategies and best practices for agile teams to enhance their cloud-native security posture.
Understanding Cloud-Native Security
Before diving into specific security tips, it’s crucial to grasp what cloud-native security entails. Cloud-native security focuses on protecting applications that are designed and deployed in the cloud, utilizing microservices, containers, and dynamic orchestration environments like Kubernetes. It emphasizes the following core principles:
- Shared Responsibility: Security is a shared responsibility between cloud service providers and users.
- Automation: Automating security measures is essential to keep pace with rapid development cycles.
- Visibility: Achieving end-to-end visibility across all components is critical for identifying vulnerabilities.
- Compliance: Ensuring adherence to regulatory standards and best practices is a must.
1. Implement Security as Code
In a cloud-native environment, infrastructure and application configurations are often defined through code. This offers an excellent opportunity to integrate security practices directly into the development process. Here are ways to implement security as code:
1.1 Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Infrastructure as Code tools, such as Terraform or AWS CloudFormation, allow teams to manage infrastructure through code. This approach enables:
- Version control for infrastructure changes.
- Automated security checks during the deployment process.
- Consistent configuration across environments.
1.2 Embed Security Policies
By embedding security policies into IaC templates, teams can enforce security standards from the outset. This can include:
- Specifying allowed network configurations.
- Defining access controls and permissions.
- Ensuring encryption is enabled for sensitive data.
2. Secure the CI/CD Pipeline
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines are vital in agile development. Securing these pipelines is essential to prevent vulnerabilities from being introduced into production environments. Consider the following strategies:
2.1 Integrate Security Testing
Automating security testing as part of the CI/CD process can help identify vulnerabilities early. Implement the following types of testing:
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST): Analyzes source code for vulnerabilities.
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST): Tests running applications for security weaknesses.
- Software Composition Analysis (SCA): Scans for vulnerabilities in third-party libraries and dependencies.
2.2 Control Pipeline Access
Limit access to the CI/CD pipeline to only essential personnel. Apply the principle of least privilege:
| Role | Access Level |
|---|---|
| Developers | Code contributions and testing environments |
| DevOps Engineers | Deployment and monitoring configurations |
| Security Team | Review and audit access logs |
3. Container Security Best Practices
Containers are a fundamental component of cloud-native architectures, but they also introduce specific security challenges. To secure containers effectively:
3.1 Use Trusted Base Images
Always start with trusted, minimal base images to reduce the attack surface. Regularly scan for vulnerabilities in these base images and keep them updated.
3.2 Apply Runtime Security Controls
Implement runtime security measures, such as:
- Monitoring for suspicious activity within containers.
- Enforcing network policies to restrict communication between containers.
- Using tools like Falco for real-time threat detection.
4. Cloud Provider Security Features
Leverage security features provided by your cloud service provider. Most major platforms offer robust security solutions, including:
4.1 Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Implement strict IAM policies to control who can access resources. Use roles and policies to define permissions and enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security.
4.2 Data Encryption
Ensure that all data, both in transit and at rest, is encrypted. Utilize cloud provider services to simplify encryption management.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
Finally, continuous monitoring and a solid incident response plan are vital for maintaining security in a cloud-native environment. Consider these actions:
5.1 Monitor Logs and Metrics
Implement a comprehensive logging and monitoring strategy to track application performance and security incidents. Tools such as:
- Cloud-native monitoring solutions (e.g., AWS CloudTrail, Azure Monitor)
- Third-party services (e.g., Splunk, Datadog)
5.2 Develop an Incident Response Plan
Prepare for potential security incidents by developing and regularly updating an incident response plan. This plan should include:
- Identification: How to detect and categorize incidents.
- Containment: Steps to limit the impact of a breach.
- Eradication and Recovery: Processes for removing threats and restoring services.
Conclusion
As agile teams continue to embrace cloud-native technologies, prioritizing security becomes more crucial than ever. By implementing best practices such as security as code, securing CI/CD pipelines, enhancing container security, leveraging cloud provider features, and maintaining continuous monitoring and incident response, teams can significantly reduce their risk profile. Remember, security is not a one-time task but an ongoing commitment that evolves with your cloud-native applications.
FAQ
What are cloud-native security practices for agile teams?
Cloud-native security practices include implementing security at every stage of the development lifecycle, utilizing automated security tools, and adopting a zero-trust security model to protect applications and data in the cloud.
How can agile teams enhance their cloud security posture?
Agile teams can enhance their cloud security posture by incorporating continuous security assessments, using container security solutions, and ensuring regular updates and patches to their cloud infrastructure.
What role do DevSecOps play in cloud-native security?
DevSecOps integrates security into the DevOps process, ensuring that security is a shared responsibility among development, operations, and security teams, which is crucial for maintaining secure cloud environments.
What are the common cloud-native security threats agile teams face?
Common threats include misconfigured cloud settings, insecure APIs, data breaches, and vulnerabilities in containerized applications that agile teams need to be vigilant about.
How can agile teams implement effective identity and access management (IAM) in the cloud?
Agile teams can implement effective IAM by using role-based access control (RBAC), enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA), and regularly reviewing access permissions to ensure least privilege access.
What are the best tools for cloud-native security for agile teams?
Best tools for cloud-native security include cloud security posture management (CSPM) solutions, web application firewalls (WAF), container security platforms, and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) security tools.