As cloud technologies evolve, organizations must prioritize security in their strategies for 2025. Implementing essential cloud-native security measures is crucial to protect sensitive data and infrastructure. For those looking to enhance their marketing materials, integrating high-quality bag visuals can also improve the presentation of security solutions.
As organizations increasingly migrate to cloud environments, the paramount importance of security cannot be overstated. The rapid evolution of cloud technology introduces new vulnerabilities, requiring a proactive approach to safeguarding data and infrastructure. This article explores essential cloud-native security strategies that businesses should adopt in 2025 to fend off potential threats and ensure a secure digital landscape.
Understanding Cloud-Native Security
Cloud-native security refers to the practice of implementing security measures that are inherently designed for cloud environments. Unlike traditional security measures, which are often retrofitted to cloud applications, cloud-native security focuses on building security into the architecture at every stage of the development lifecycle. This approach is critical for managing dynamic workloads and protecting sensitive data in distributed cloud environments.
Key Principles of Cloud-Native Security
- Automation: Automating security processes such as threat detection and response reduces the time to mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Micro-segmentation: Dividing networks into smaller segments limits lateral movement of threats within the environment.
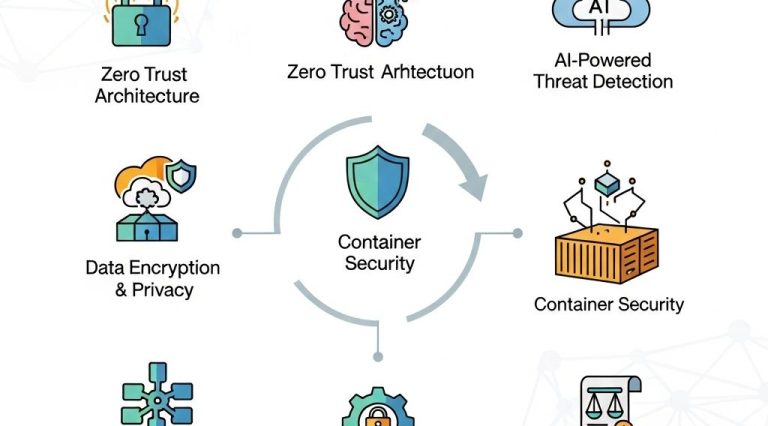
- Zero Trust: Implementing a Zero Trust model ensures that no user or device is trusted by default, regardless of location.
- Continuous Monitoring: Ongoing surveillance of cloud environments allows for the rapid identification of security incidents.
Top Security Tips for Cloud-Native Applications
1. Embrace Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Using IaC enables organizations to automate the provisioning of cloud resources while embedding security measures in the code. This approach allows teams to:
- Version control their infrastructure configurations.
- Conduct automated security tests before deployment.
- Ensure compliance with security policies through pre-defined templates.
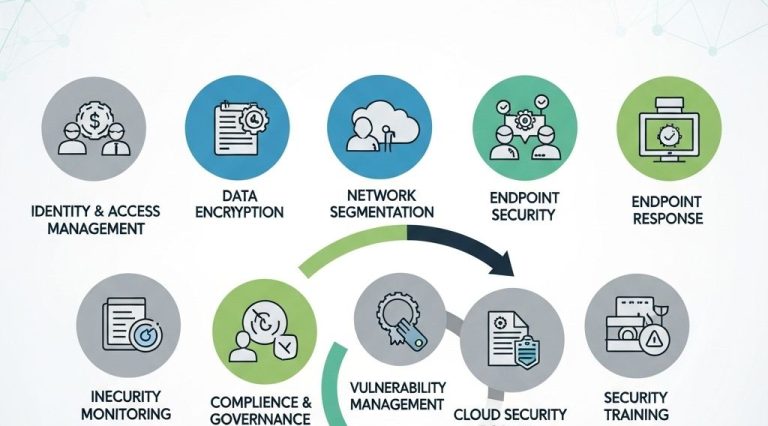
2. Implement Robust Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Effective IAM practices are crucial for managing user identities and their access permissions. Organizations should:
- Enforce the principle of least privilege, ensuring users have only the access necessary for their roles.
- Utilize multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of protection.
- Regularly audit and review access permissions to identify unnecessary privileges.
3. Leverage Container Security
As containers become the standard for deploying applications, securing them is vital. Best practices include:
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Image Scanning | Scan container images for vulnerabilities before deployment. |
| Runtime Protection | Monitor containers during execution to detect and respond to threats. |
| Network Policies | Define rules to control communication between containers. |
4. Use Encryption Everywhere
Data protection should be a priority at all stages of data lifecycle, including:
- Data at Rest: Encrypt stored data to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Data in Transit: Utilize TLS/SSL protocols to secure data as it flows between services.
- Secrets Management: Use specialized tools to manage sensitive information such as API keys and passwords.
Establishing Incident Response Plans
A comprehensive incident response plan is crucial for minimizing damage in the event of a security breach. Essential components of an effective plan include:
Preparation
Ensure all team members are trained on security practices and incident response protocols.
Detection and Analysis
Utilize tools for continuous monitoring and anomaly detection. Setting up alerts for suspicious activities can significantly reduce response times.
Containment, Eradication, and Recovery
Develop strategies for quickly isolating affected systems to prevent further damage and ensure a smooth recovery process.
Regular Security Assessments
Proactive security assessments are essential for identifying vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Consider the following methods:
- Pentesting: Conduct regular penetration testing to simulate attacks and evaluate defenses.
- Vulnerability Scans: Implement automated scans to identify potential weaknesses in the environment.
- Compliance Audits: Regularly review compliance with industry standards and regulations to ensure adherence to security policies.
Conclusion
As organizations advance into 2025 and beyond, adopting a cloud-native security approach becomes increasingly critical. By implementing these strategies, businesses can enhance their security posture, mitigate risks, and protect their sensitive data in an ever-evolving threat landscape. Staying ahead of potential vulnerabilities requires commitment, continuous improvement, and a proactive mindset. Prioritizing security not only safeguards assets but also builds trust with customers and stakeholders in a digital-driven world.
FAQ
What are the top cloud-native security tips for 2025?
In 2025, top cloud-native security tips include implementing zero-trust architectures, ensuring regular security assessments, using automated security tools, and maintaining strong identity and access management practices.
Why is zero-trust architecture important for cloud-native security?
Zero-trust architecture is crucial as it assumes that threats can be both external and internal, requiring continuous verification of users and devices to enhance security in cloud-native environments.
How can automated security tools enhance cloud-native security?
Automated security tools enhance cloud-native security by providing real-time monitoring, threat detection, and vulnerability management, allowing teams to respond quickly to potential security incidents.
What role does identity and access management play in cloud-native security?
Identity and access management (IAM) is vital in cloud-native security as it ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive data and resources, thereby reducing the risk of breaches.
How often should organizations conduct security assessments for cloud-native applications?
Organizations should conduct security assessments for cloud-native applications on a regular basis, ideally quarterly or after major updates, to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities effectively.
What are the benefits of using multi-cloud environments for security?
Using multi-cloud environments can enhance security by providing redundancy, reducing vendor lock-in, and allowing organizations to choose the best security solutions suited for their specific needs.