As businesses prepare for the evolving landscape of cloud-native security in 2025, adopting a proactive approach is essential. This includes integrating security at every stage of development while utilizing tools and resources that enhance security measures. For instance, designers can boost their creative process with designer bag templates that streamline project workflows, allowing teams to focus more on security innovations.
As organizations continue to migrate to cloud-native architectures, ensuring robust security practices is more critical than ever. The shift to cloud environments presents unique challenges and opportunities, necessitating a reevaluation of traditional security measures. In this article, we will explore key cloud-native security practices that are poised to dominate in 2025, enabling organizations to protect their assets effectively while harnessing the full potential of cloud technologies.
Understanding Cloud-Native Security
Cloud-native security refers to the practices and technologies that secure applications built specifically for cloud environments. Unlike traditional security models, which often rely on perimeter defenses, cloud-native security emphasizes automation, visibility, and continuous monitoring. This paradigm shift is driven by the dynamic and flexible nature of cloud services, which necessitates a more integrated approach to security.
The Importance of a Security-first Mindset
Embracing a security-first mindset is vital for organizations transitioning to cloud-native architectures. This means prioritizing security at every stage of the development lifecycle, from inception to deployment and beyond. Below are some critical components of a security-first mindset:
- Integration: Security should be integrated into DevOps processes (DevSecOps) to ensure that security is a continuous consideration.
- Collaboration: Teams should work together across development, operations, and security to identify and mitigate risks early.
- Automation: Automating security checks can speed up the development process while reducing human error.
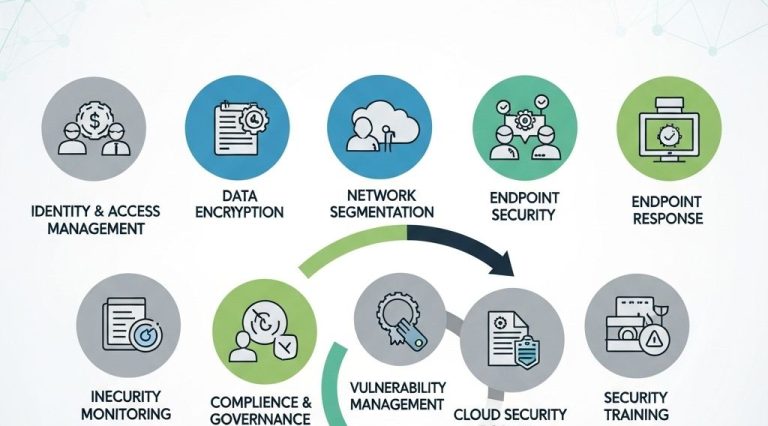
Key Security Practices for 2025
Below are some of the leading security practices organizations should adopt to enhance their cloud-native security posture in 2025:
1. Shift Left Security
Shifting security left in the development process means integrating security measures early on. This practice helps identify vulnerabilities before code is deployed. Key strategies include:
- Conducting threat modeling during the design phase.
- Implementing static application security testing (SAST) during development.
- Utilizing software composition analysis (SCA) to identify vulnerabilities in third-party libraries.
2. Zero Trust Architecture
Adopting a Zero Trust approach involves verifying every request regardless of whether it originates from inside or outside the organization. Characteristics of a Zero Trust architecture include:
- Least privilege access controls to minimize user permissions.
- Micro-segmentation to limit lateral movement within networks.
- Continuous identity verification and authentication.
3. Container Security
Containers have become a popular choice for deploying applications in cloud environments. However, they also introduce new security challenges. To ensure container security, organizations should:
- Scan images for vulnerabilities before deployment.
- Implement runtime security policies to monitor and protect containers in production.
- Employ tools like Kubernetes security policies to enforce security standards.
4. Secure Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) enables organizations to manage and provision infrastructure through code, making it crucial to secure these configurations. Best practices include:
- Utilizing code review processes to detect misconfigurations.
- Incorporating security tools in CI/CD pipelines to automate compliance checks.
- Implementing version control for IaC templates to track changes and mitigate risks.
5. Advanced Threat Detection and Response
With the rise of sophisticated cyber threats, organizations must invest in advanced threat detection and response capabilities. Key components include:
- Implementing Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems for real-time monitoring.
- Utilizing Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for anomaly detection.
- Establishing an incident response plan that outlines procedures for detecting, responding to, and recovering from security incidents.
Integrating Compliance into Security Practices
Compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS is crucial for maintaining customer trust and avoiding penalties. In 2025, organizations must:
- Automate compliance checks to ensure ongoing adherence to regulations.
- Conduct regular audits of security practices and compliance policies.
- Incorporate compliance requirements into the development process.
The Role of Security Tools and Technologies
Incorporating the right tools and technologies is essential for implementing effective cloud-native security practices. Here are some tools that will gain prominence in 2025:
| Tool | Functionality | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Container Security Scanners | Identify vulnerabilities in container images. | Enhances security posture pre-deployment. |
| CI/CD Security Automation Tools | Automate security checks within CI/CD pipelines. | Reduces manual errors and speeds up deployment. |
| SIEM Solutions | Aggregate and analyze security event data. | Improves threat detection capabilities. |
Building a Culture of Security Awareness
Beyond tools and technologies, cultivating a security-aware culture within the organization is paramount. Organizations should:
- Provide regular security training and awareness programs for employees.
- Encourage reporting of security incidents without fear of reprisal.
- Promote the sharing of security knowledge across teams.
Conclusion
As we move into 2025, the landscape of cloud-native security will continue to evolve. By adopting forward-thinking practices such as shift left security, Zero Trust architecture, and advanced threat detection, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture. Emphasizing a culture of security awareness and incorporating the right tools and technologies will be crucial in navigating the challenges ahead. Embrace these practices today to secure your cloud-native future.
FAQ
What are cloud-native security practices?
Cloud-native security practices are strategies and tools designed to protect applications and data in cloud environments, focusing on automation, integration, and continuous monitoring throughout the development lifecycle.
Why is cloud-native security important for businesses in 2025?
As businesses increasingly rely on cloud services, cloud-native security is essential to protect sensitive data, ensure compliance with regulations, and mitigate risks associated with cyber threats.
What are the top cloud-native security practices for 2025?
Top cloud-native security practices for 2025 include implementing zero-trust architecture, using automated security tools, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, and ensuring secure coding practices.
How can organizations implement zero-trust security in cloud-native environments?
Organizations can implement zero-trust security by verifying every request, enforcing least-privilege access controls, and continuously monitoring user activities and system interactions.
What role does automation play in cloud-native security?
Automation plays a crucial role in cloud-native security by enabling faster responses to threats, streamlining compliance checks, and reducing human error through automated security testing and monitoring.
How do organizations ensure compliance with regulations in cloud-native security?
Organizations can ensure compliance by adopting security frameworks, conducting regular audits, automating compliance checks, and staying updated on changing regulations relevant to their industry.