In an era where agile workflows are critical, understanding the intersection of cloud-native technologies and security is paramount. As businesses strive to enhance their responsiveness, they can also draw inspiration from innovative design approaches, such as eco-friendly bag designs, that reflect sustainability and forward-thinking practices.
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, organizations are increasingly adopting cloud-native technologies to enhance their agility and responsiveness to market changes. While cloud-native applications bring numerous advantages, they also introduce unique security challenges that must be addressed to ensure organizational integrity and data protection. This article explores the key aspects of cloud-native security and how organizations can effectively bolster their agile workflows through robust security practices.
Understanding Cloud-Native Security
Cloud-native security refers to the practices and tools used to secure applications that are built and deployed in cloud environments. Unlike traditional security models, which often rely on perimeter defenses, cloud-native security is integrated throughout the application lifecycle. This approach emphasizes:
- Automation of security controls
- Continuous monitoring
- Microservices architecture
- DevSecOps integration
The Importance of Shifting Security Left
Shifting security left means integrating security practices early in the software development lifecycle. This proactive measure helps identify vulnerabilities and security issues before they reach production. Benefits of this approach include:
- Reduced costs associated with late-stage security fixes
- Faster deployment cycles
- Enhanced collaboration between development and security teams
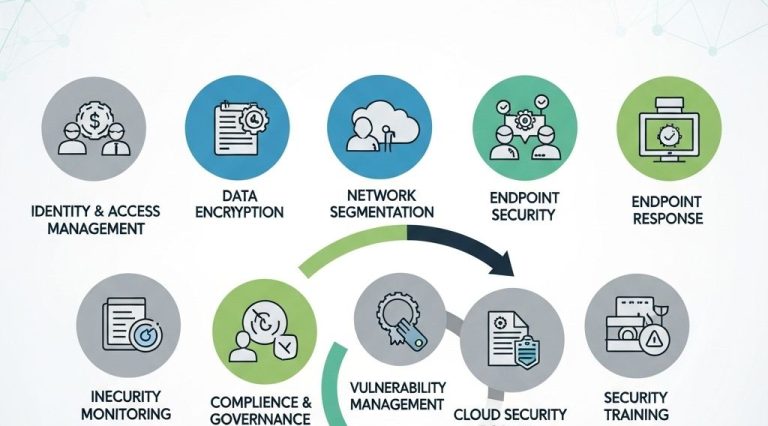
Key Security Principles for Cloud-Native Environments
To effectively secure cloud-native applications, organizations should adhere to several core principles:
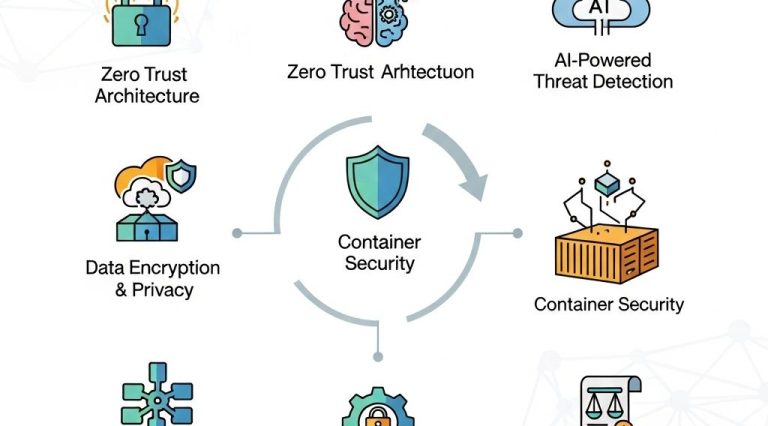
1. Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust is a security model that operates under the premise that threats could originate from both outside and inside the network. Key components include:
- Identity and access management (IAM)
- Micro-segmentation
- Continuous authentication
2. Defense in Depth
This principle advocates for multiple layers of security controls, which may include:
| Layer | Security Control |
|---|---|
| Network | Firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) |
| Application | Web Application Firewalls (WAFs), Secure Coding Practices |
| Data | Encryption, Data Loss Prevention (DLP) |
3. Automated Security Testing
Incorporating automated security testing tools throughout the CI/CD pipeline ensures that security checks are consistently applied. Types of tests include:
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) scanning
Implementing Cloud-Native Security Best Practices
The implementation of cloud-native security best practices can significantly enhance the security posture of an organization:
1. Secure Application Development
Developers should be trained in secure coding guidelines and use frameworks that emphasize security. Regular code reviews and pair programming can also facilitate security awareness.
2. Infrastructure Security
Use tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation to implement Infrastructure as Code (IaC). This approach allows teams to manage and provision cloud resources securely and consistently.
3. Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
Utilize security information and event management (SIEM) tools to continuously monitor applications for suspicious activity. In addition, establish an incident response plan tailored for cloud-native environments.
Challenges in Cloud-Native Security
Despite the advantages of cloud-native security, organizations may face several challenges, including:
1. Complexity of Microservices
The microservices architecture, while beneficial for agility, can complicate security. Each service may have its security requirements, necessitating detailed oversight.
2. Data Privacy Regulations
Organizations must navigate various data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) that impact how customer data is stored and processed in the cloud.
3. Evolving Threat Landscape
The rapid evolution of cyber threats requires continuous adaptation of security measures and practices.
Future Trends in Cloud-Native Security
As technology advances, cloud-native security will evolve. Here are some trends to watch:
1. Increased Use of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning algorithms can enhance threat detection and response capabilities, allowing organizations to identify anomalies faster.
2. Greater Emphasis on Compliance Automation
Automation tools will play a vital role in ensuring compliance with regulations, helping organizations to manage their risk better.
3. Collaborative Security Models
Security will become a shared responsibility between development, operations, and security teams, promoting a culture of security across the organization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud-native security is an essential component of modern software development that enables organizations to maintain agility while securing their applications. By adopting best practices, understanding the principles of cloud-native security, and staying ahead of emerging trends, organizations can effectively navigate the complexities of securing cloud environments. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, prioritizing security will not only protect sensitive data but also empower organizations to innovate and compete in an ever-changing market.
FAQ
What is cloud-native security?
Cloud-native security refers to the practices and technologies used to secure applications and infrastructure that are built and deployed in cloud environments, emphasizing automation and scalability.
How does cloud-native security enhance agile workflows?
Cloud-native security enhances agile workflows by integrating security measures directly into the development process, allowing for faster deployment cycles while ensuring that security is maintained throughout.
What are the key principles of cloud-native security?
Key principles of cloud-native security include automation, continuous monitoring, compliance as code, and a strong focus on identity and access management.
Why is automation important in cloud-native security?
Automation is crucial in cloud-native security as it helps streamline security processes, reduce human error, and enable faster response to threats, ultimately supporting agile methodologies.
What are some best practices for implementing cloud-native security?
Best practices for implementing cloud-native security include adopting a zero-trust model, integrating security into CI/CD pipelines, utilizing micro-segmentation, and regularly updating and patching software.
How can organizations measure the effectiveness of their cloud-native security?
Organizations can measure the effectiveness of their cloud-native security by tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as incident response times, vulnerability detection rates, and compliance adherence.