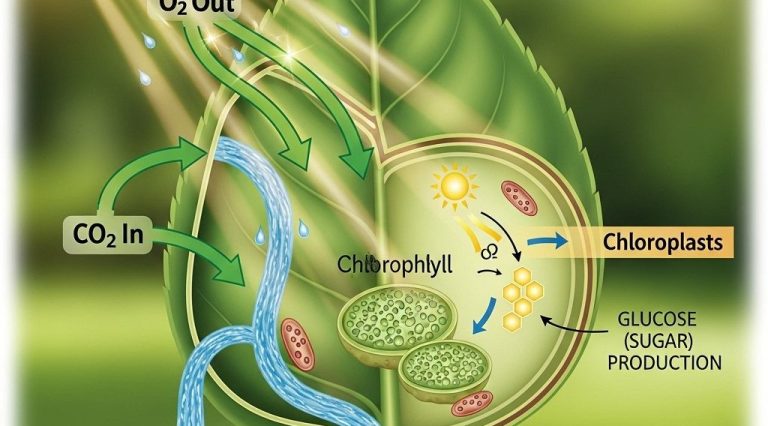
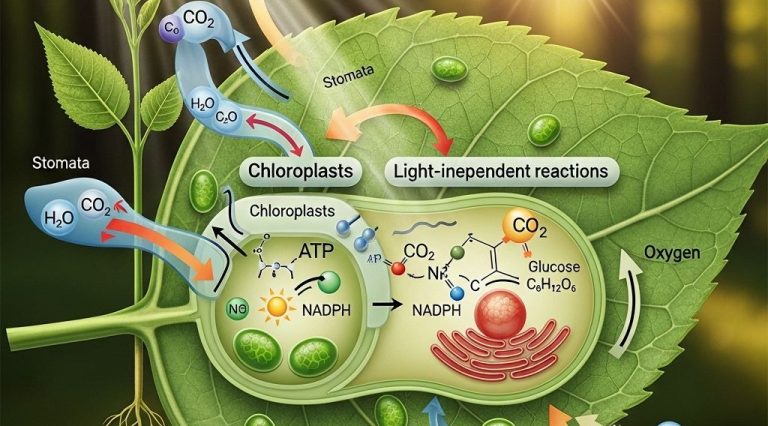
Astrobiology captivates many with its exploration of life beyond Earth, merging disciplines like biology and astronomy. As investigators delve into environments once deemed uninhabitable, we uncover potential parallels that may influence innovative design, such as eco-friendly bag designs. This intersection of science and creativity showcases our quest to understand life’s possibilities across the cosmos.
Astrobiology is an interdisciplinary field that explores the potential for life beyond Earth. This fascinating branch of science combines elements of biology, astronomy, geology, and chemistry to understand the conditions that support life. As we continue to explore our solar system and beyond, several intriguing facts about astrobiology emerge. Here are some of the key insights that every tech-savvy individual should know.
The Origins of Life
One of the primary questions astrobiology seeks to answer is how life originated. Theories range from:
- Abiogenesis: Life arising from non-living matter through natural processes.
- Panspermia: Life spreading throughout the universe via comets, asteroids, or meteorites.
- Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vents: The possibility that life began in extreme environments on Earth.
Key Terms Related to Origins
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Abiogenesis | The natural process where life arises from non-living matter. |
| Panspermia | The hypothesis that life exists throughout the universe and is distributed by space dust, meteoroids, or comets. |
| Hydrothermal Vents | Natural openings in the Earth’s surface that emit heated water, potentially supporting diverse ecosystems. |
Life in Extreme Conditions
Astrobiologists study extremophiles—organisms that thrive in conditions previously thought to be uninhabitable. Some notable extremophiles include:
- Thermophiles: Live in high-temperature environments like hot springs.
- Halophiles: Thrive in highly saline environments, such as salt lakes.
- Acidophiles: Favor acidic conditions, often found in sulfuric lakes.
Implications for Extraterrestrial Life
The existence of extremophiles on Earth suggests that life could potentially exist in similar extreme environments on other planets, such as:
- Europa: Jupiter’s moon, believed to have a subsurface ocean beneath its icy crust.
- Enceladus: Saturn’s moon, which also has geysers ejecting water vapor and organic compounds.
- Mars: Evidence of past water flow and current subsurface water increases the potential for microbial life.
Search for Exoplanets
The discovery of exoplanets—planets outside our solar system—has transformed our understanding of where life could exist. Key points include:
- Habitable Zone: The region around a star where conditions may be just right for liquid water to exist.
- TESS and Kepler Missions: NASA missions that have significantly increased the catalog of known exoplanets.
- Transiting Method: A technique used to find exoplanets by measuring the dimming of stars as planets pass in front of them.
Current Exoplanet Discoveries
As of 2023, thousands of exoplanets have been discovered, with varying characteristics. Among them:
| Planet Name | Star System | Size | Potential Habitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proxima Centauri b | Proxima Centauri | Earth-sized | Possibly |
| TRAPPIST-1 e | TRAPPIST-1 | Earth-sized | Possibly |
| Kepler-186f | Kepler-186 | Earth-sized | Possibly |
Astrobiology and Mars
Mars has been a primary focal point for astrobiological research due to its similarities to Earth:
- Water Presence: Evidence of ancient riverbeds, polar ice, and possible briny subsurface water.
- Robotic Missions: Rovers like Curiosity and Perseverance are equipped with tools to detect signs of past microbial life.
- Future Missions: Plans for human exploration may help answer the question of whether life ever existed on Mars.
Rover Technologies
Recent rover advancements include:
- Sample Collection: Rovers can collect and cache samples for future return missions.
- Autonomous Navigation: Increased autonomy allows rovers to navigate challenging terrains without real-time human input.
- Advanced Instruments: Equipped with spectrometers to analyze soil and rock samples for organic materials.
The Fermi Paradox
The Fermi Paradox poses a compelling question: If the universe is so vast and potentially full of life, why haven’t we found any evidence of extraterrestrial civilizations? Some theories addressing this paradox are:
- Rare Earth Hypothesis: Suggests that Earth-like planets with life are incredibly rare.
- Great Filter: The idea that there is a stage in the evolution of life that is extraordinarily hard for life to pass.
- Technological Singularity: Advanced civilizations may self-destruct or transcend the need for physical communication.
Impacts on Future Research
Understanding the Fermi Paradox influences astrobiological research, leading to the development of new technologies and methods for detecting potential extraterrestrial signals.
Astrobiology and Artificial Intelligence
AI is increasingly becoming a pivotal tool in astrobiology research, assisting in:
- Data Analysis: Processing vast amounts of astronomical data to identify patterns and anomalies.
- Simulations: Creating models to simulate environments where life could exist.
- Machine Learning: Improving the accuracy of exoplanet detection through predictive algorithms.
Future of AI in Astrobiology
As technology progresses, the integration of AI into astrobiological research is expected to enhance our understanding of the universe and the quest for extraterrestrial life.
Conclusion
Astrobiology is a field that combines scientific inquiry with the ultimate question of our existence: Are we alone in the universe? By exploring the origins of life, studying extreme environments, and investigating exoplanets, we are piecing together the cosmic puzzle. As technology advances and our understanding deepens, the quest for extraterrestrial life continues to inspire both scientists and the public alike. The journey of discovery is just beginning, and the potential findings may reshape our understanding of life itself.
FAQ
What is astrobiology?
Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe.
How does astrobiology relate to the search for extraterrestrial life?
Astrobiology combines multiple scientific disciplines to understand the potential for life beyond Earth, guiding missions to find signs of life on other planets and moons.
What are extremophiles and why are they important in astrobiology?
Extremophiles are organisms that can survive in extreme conditions, providing insights into how life might exist on other planets with harsh environments.
What role do planets like Mars and Europa play in astrobiological research?
Mars and Europa are key targets for astrobiology due to evidence of past water, which may have supported life, as well as current missions aimed at discovering biosignatures.
How do scientists search for biosignatures in space?
Scientists use telescopes and space missions to analyze the atmospheres of exoplanets and look for chemical indicators of life, known as biosignatures.
What is the significance of the Drake Equation in astrobiology?
The Drake Equation estimates the number of active extraterrestrial civilizations in the Milky Way, helping to frame the search for intelligent life in the universe.