In today’s rapidly evolving tech landscape, understanding the core concepts of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) is essential for anyone looking to stay informed. These technologies have widespread applications across various industries, and having access to resources, such as high-quality bag visuals, can enhance visual comprehension and engagement when exploring complex topics.
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) are terms that have become ubiquitous in today’s tech-driven landscape. They drive innovations across various sectors, from healthcare to finance, and are at the core of modern technological advancements. Understanding the distinctions and relationships among these concepts is crucial for harnessing their potential effectively.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, particularly computer systems. It encompasses a broad range of technologies and applications, aiming to create systems that can perform tasks requiring human intelligence.
Key Components of AI
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enables machines to understand and respond to human language.
- Robotics: Involves designing and programming robots to perform various tasks.
- Computer Vision: Allows machines to interpret and process visual information from the world.
- Expert Systems: Mimic the decision-making abilities of a human expert.
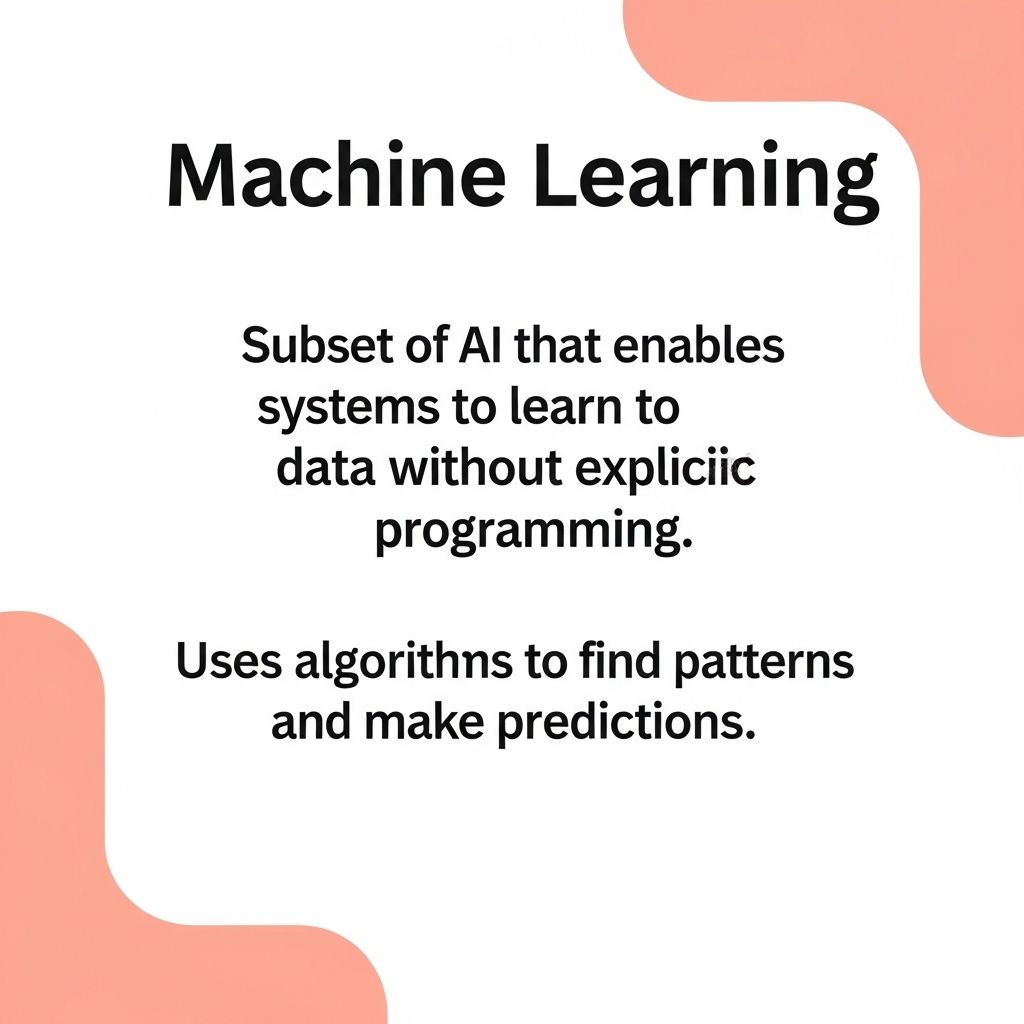
Understanding Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on the development of algorithms that enable computers to learn from and make predictions based on data. Unlike traditional programming, where the rules are explicitly programmed, ML systems learn patterns from data to improve their performance over time.
Types of Machine Learning
- Supervised Learning: Involves training a model on a labeled dataset, where the correct output is known. Examples include classification and regression tasks.
- Unsupervised Learning: Involves training a model on an unlabeled dataset, where the system attempts to identify patterns or groupings without pre-existing labels. Common techniques include clustering and association.
- Reinforcement Learning: An area of ML where an agent learns to make decisions by taking actions in an environment to maximize some notion of cumulative reward.
Diving into Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a subset of ML that utilizes neural networks with many layers (also known as deep neural networks) to process data. It mimics the human brain’s structure and function, allowing for higher levels of abstraction and complexity in learning tasks.
How Deep Learning Works
Deep Learning algorithms learn representations of data through multiple layers of abstraction. The architecture of a deep learning model consists of:
| Layer Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Input Layer | The first layer that receives the raw input data. |
| Hidden Layers | Intermediate layers that perform computations and extract features from the data. |
| Output Layer | The final layer that produces the desired output, such as class probabilities. |
Comparing AI, ML, and DL
To clarify the distinctions between AI, ML, and DL, let’s look at a comparative overview:
| Feature | Artificial Intelligence | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broad field encompassing various technologies | A specific subset of AI focused on data-driven learning | A subset of ML using neural networks for complex problem-solving |
| Data Dependency | Can be rule-based and doesn’t require data | Requires data to train models | Needs large amounts of data for effective training |
| Complexity | Varies widely | Less complex than DL | Highly complex with multiple layers of abstraction |
Applications in Real Life
The applications of AI, ML, and DL are vast and impact various domains:
Healthcare
- Predictive analytics for patient diagnosis and treatment.
- Image analysis for medical imaging diagnostics.
- Personalized medicine based on individual patient data.
Finance
- Fraud detection through anomaly detection algorithms.
- Algorithmic trading based on market data analysis.
- Risk management using predictive modeling.
Transportation
- Self-driving cars utilizing computer vision and reinforcement learning.
- Traffic management systems using predictive analytics.
- Route optimization for logistics and delivery services.
Future Trends in AI, ML, and DL
The future of AI, ML, and DL is promising with several emerging trends:
Explainable AI
As AI systems become more complex, the demand for transparency in how they make decisions will grow. Explainable AI aims to make AI systems’ decision-making processes understandable to humans.
Federated Learning
This trend involves training algorithms across multiple decentralized devices or servers holding local data samples, without exchanging them. It enhances privacy and reduces the need for centralized data storage.
Edge AI
Edge AI refers to the deployment of AI algorithms on edge devices, enabling real-time data processing without relying on cloud computing.
Conclusion
The advancements in AI, ML, and DL continue to redefine numerous industries and enhance human capabilities. As these technologies evolve, embracing their potential while addressing ethical considerations will be vital in shaping a future that benefits everyone.
FAQ
What is the difference between AI, machine learning, and deep learning?
AI refers to artificial intelligence, which encompasses any technique that enables machines to mimic human behavior. Machine learning is a subset of AI that involves algorithms that learn from data to make predictions or decisions. Deep learning, a further subset of machine learning, uses neural networks with many layers to analyze various forms of data.
How does machine learning work?
Machine learning works by training algorithms on large datasets, allowing them to identify patterns and make predictions or decisions based on new data. It typically involves supervised learning (using labeled data), unsupervised learning (using unlabeled data), or reinforcement learning (using rewards to guide learning).
What are the applications of deep learning?
Deep learning is used in various applications, including image and speech recognition, natural language processing, autonomous vehicles, and medical diagnosis. Its ability to process vast amounts of unstructured data makes it particularly powerful in these areas.
Is AI the same as automation?
No, AI and automation are not the same. Automation refers to the use of technology to perform tasks without human intervention, while AI involves the ability of a system to learn from data and improve its performance over time.
What skills are needed to work in AI and machine learning?
Key skills required for a career in AI and machine learning include programming (especially in Python and R), data analysis, statistics, linear algebra, and a solid understanding of algorithms and machine learning frameworks.