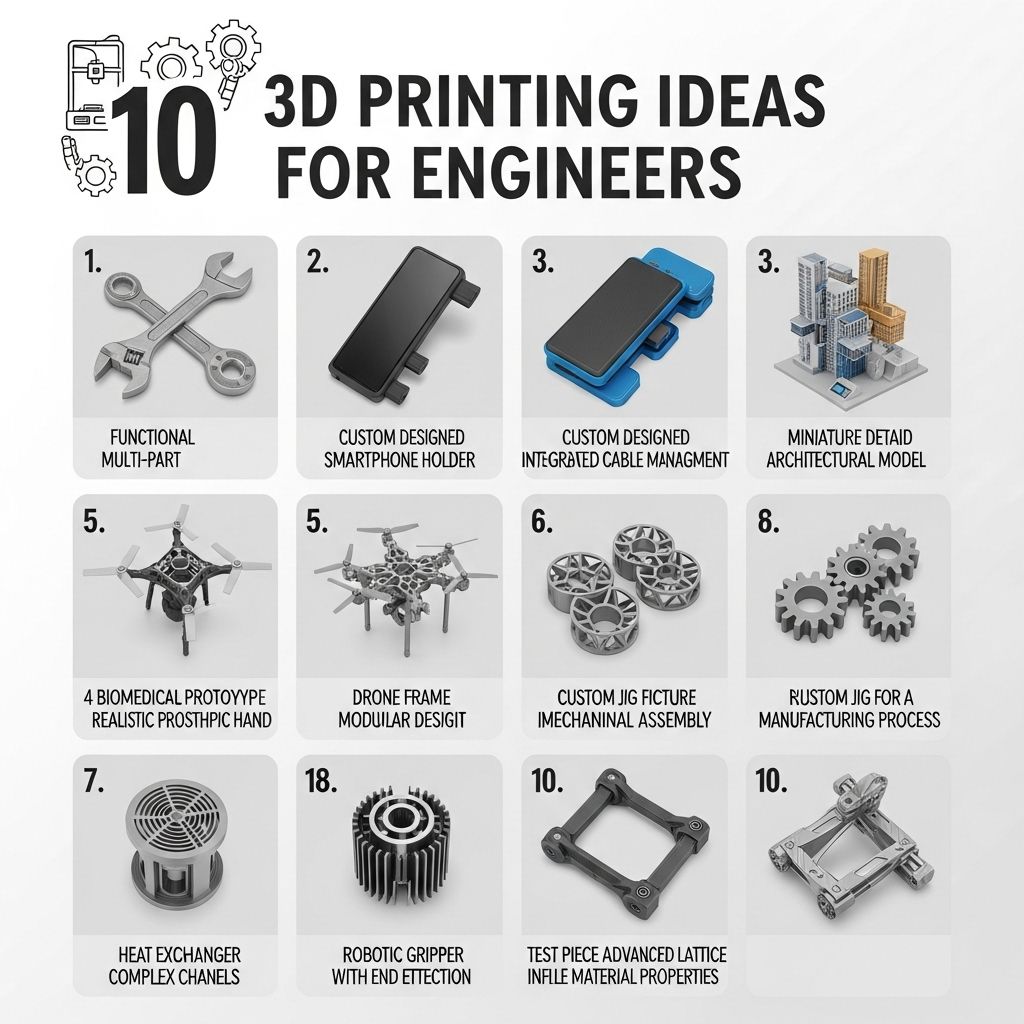
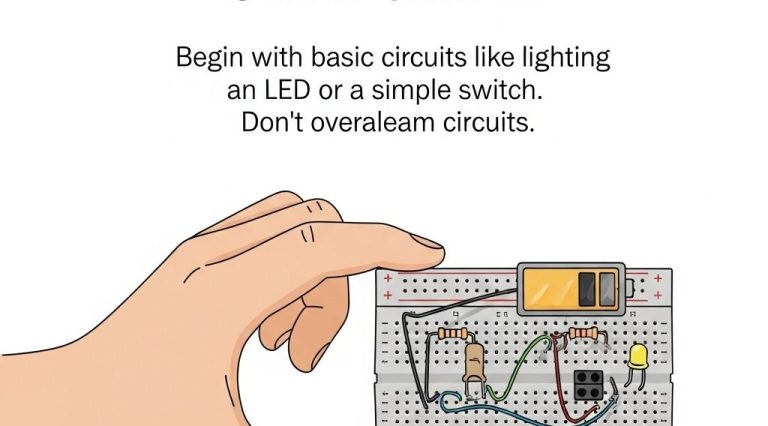
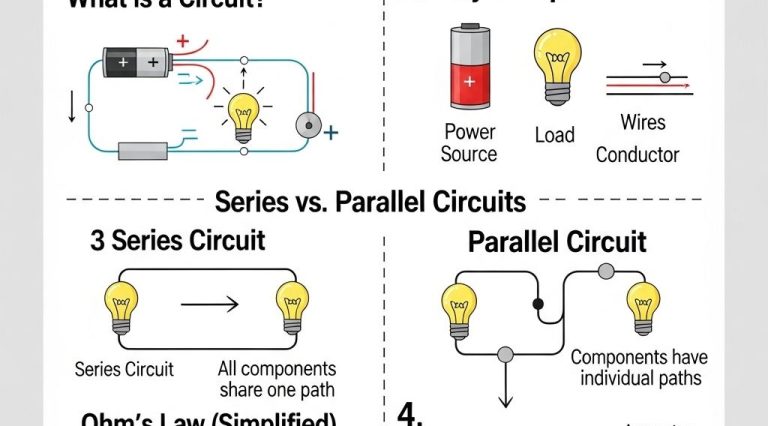
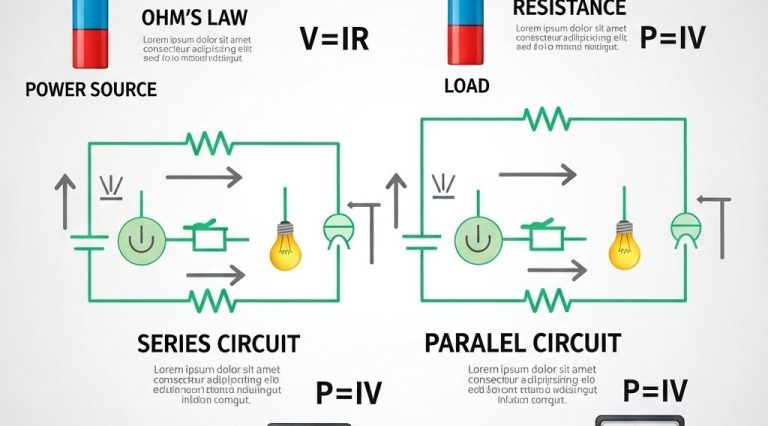
In the realm of engineering, innovative advancements are often sparked by the integration of emerging technologies. One such game changer is 3D printing, which not only facilitates rapid prototyping but also fosters a culture of creativity and experimentation. As engineers explore creative design concepts through 3D printing, they unlock the potential for groundbreaking projects that redefine traditional manufacturing techniques.
In the rapidly evolving world of engineering and technology, 3D printing has emerged as a revolutionary tool that allows for rapid prototyping, customization, and innovative production techniques. Engineers across various fields are harnessing the power of 3D printing to bring their ideas to life, streamline their processes, and reduce costs. This article explores ten inspiring 3D printing ideas that engineers can incorporate into their projects, highlighting the versatility and practicality of this remarkable technology.
1. Custom Tooling
One of the most immediate applications of 3D printing in engineering is the creation of custom tooling. Traditional manufacturing methods can be time-consuming and costly, especially for unique or low-volume tools. With 3D printing, engineers can design and produce tools tailored to specific tasks or projects. Benefits include:
- Reduced lead times for tool production.
- Lower costs for one-off or specialized tools.
- Increased design flexibility.
Example Applications:
Engineers can create jigs, fixtures, or even molds that fit precisely to their specifications. This is particularly beneficial for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing.
2. Prototyping Complex Geometries
3D printing enables engineers to prototype complex geometries that would be impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. This allows for:
- Rapid iteration of designs.
- Testing and validation of innovative concepts.
- Enhanced creativity in design processes.
Benefits of Complex Prototyping:
Engineers can experiment with intricate designs such as organic shapes, lattice structures, and lightweight components that can significantly enhance performance.
3. Replacement Parts
In engineering, the ability to quickly produce replacement parts can save time and resources. 3D printing allows for:
- On-demand production of components.
- Reduced inventory costs.
- Customization for specific applications.
Industries that Benefit:
Manufacturing, automotive, and even medical fields often rely on 3D printing to replace or repair parts with minimal downtime.
4. Educational Models
3D printing is an invaluable resource for educational purposes. Engineers and educators can create:
- Scale models of complex systems or structures.
- Hands-on learning tools for students.
- Visual aids for presentations or demonstrations.
Examples of Educational Models:
Architecture students can benefit from 3D printed models of buildings, while mechanical engineering students can visualize intricate machine components.
5. Lightweight Components
Weight reduction is crucial in various engineering fields, particularly in aerospace and automotive industries. 3D printing facilitates the creation of lightweight components through:
- Lattice structures that maintain strength while reducing material usage.
- Optimization techniques that enhance aerodynamic performance.
Why Lightweight Matters:
Reducing weight can lead to increased fuel efficiency, improved performance, and reduced manufacturing costs.
6. Medical Devices
In the healthcare sector, 3D printing is transforming the creation of medical devices. Engineers can design and produce:
- Custom prosthetics that fit patients perfectly.
- Surgical models for preoperative planning.
- Biocompatible implants tailored to individual needs.
Impact on Healthcare:
This customization leads to better patient outcomes and reduced surgical times.
7. Architectural Elements
In architecture and construction, 3D printing is making waves by enabling the production of unique architectural elements. Engineers can create:
- Intricate facades that are both aesthetically pleasing and functional.
- Custom interior elements such as staircases or furniture.
Benefits for Architectural Design:
This technology promotes creativity in design and allows for the exploration of unconventional shapes and materials.
8. Robotics Components
As the field of robotics continues to grow, 3D printing plays a significant role in developing complex robotic components. Engineers can design:
- Custom parts that enhance functionality.
- Lightweight frames for agility and speed.
- Integrated circuits and sensors for advanced robotics.
Robotics Applications:
From drones to industrial robots, the customization and optimization possibilities are nearly limitless.
9. Art and Design Projects
3D printing is also a powerful tool for artists and designers looking to push the boundaries of traditional art forms. Engineers can collaborate with artists to create:
- Unique sculptures with intricate details.
- Functional art pieces that bridge the gap between aesthetics and utility.
Artistic Applications:
This fusion of engineering and art leads to innovative creations that challenge conventional perceptions.
10. Sustainable Products
With a growing emphasis on sustainability, 3D printing can help engineers create eco-friendly products by:
- Utilizing recycled materials for printing.
- Minimizing waste through additive manufacturing processes.
- Designing products that are easier to recycle or repurpose.
Benefits of Sustainable Engineering:
Engineers have the opportunity to contribute to a greener future while meeting the demands of conscious consumers.
Conclusion
3D printing offers incredible opportunities for engineers to innovate across various fields. From creating custom tools and complex prototypes to developing sustainable products and medical devices, the applications are varied and impactful. As technology continues to evolve, it will be exciting to see how engineers leverage 3D printing to push the boundaries of what’s possible, driving progress and redefining industries. By embracing these ten ideas, engineers can not only enhance their projects but also contribute to a more efficient and sustainable future.
FAQ
What are some innovative 3D printing ideas for engineers?
Engineers can explore creating custom drone parts, prototyping complex mechanical assemblies, designing ergonomic tools, fabricating lightweight structures, and developing specialized jigs and fixtures.
How can 3D printing help in prototyping for engineering projects?
3D printing allows engineers to create rapid prototypes, enabling faster iteration and testing of designs, which can significantly reduce development time and costs.
What materials are commonly used in 3D printing for engineering applications?
Common materials include PLA, ABS, PETG, nylon, and specialized filaments like carbon fiber or metal-infused materials for enhanced strength and durability.
Can 3D printing be used for producing functional parts in engineering?
Yes, 3D printing can be used to produce functional parts, especially with advanced materials and techniques that meet specific mechanical and thermal properties required for engineering applications.
What are the advantages of using 3D printing in engineering design?
Advantages include reduced material waste, the ability to create complex geometries, faster turnaround times, and the potential for customization that traditional manufacturing methods cannot achieve.