In today’s tech-driven landscape, understanding microcontrollers is essential for anyone looking to innovate in the electronics field. Just like how custom bags come in various designs for different purposes, microcontrollers can be tailored for a wide range of applications, empowering creators to build smarter devices.
Microcontrollers are integral components in the modern world of electronics, serving as the brain behind countless devices we use daily, from household appliances to complex robotics. Understanding microcontrollers can empower you to innovate, automate, and create smarter devices. This article breaks down the journey of mastering microcontrollers into five essential steps.
Step 1: What is a Microcontroller?
A microcontroller is a compact integrated circuit designed to govern a specific operation in an embedded system. Unlike a traditional microprocessor, which requires additional components to function, a microcontroller contains:
- A processor core
- Memory (both RAM and ROM)
- Input and output peripherals
Microcontrollers enable devices to process data and communicate with other components efficiently. They operate on a single chip, offering a cost-effective solution for various applications.
Types of Microcontrollers
Microcontrollers can be categorized based on various factors:
| Type | Architecture | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 8-bit | Simple architecture | Home appliances, toys |
| 16-bit | Moderate complexity | Automotive, industrial control |
| 32-bit | Advanced processing | Smartphones, IoT devices |
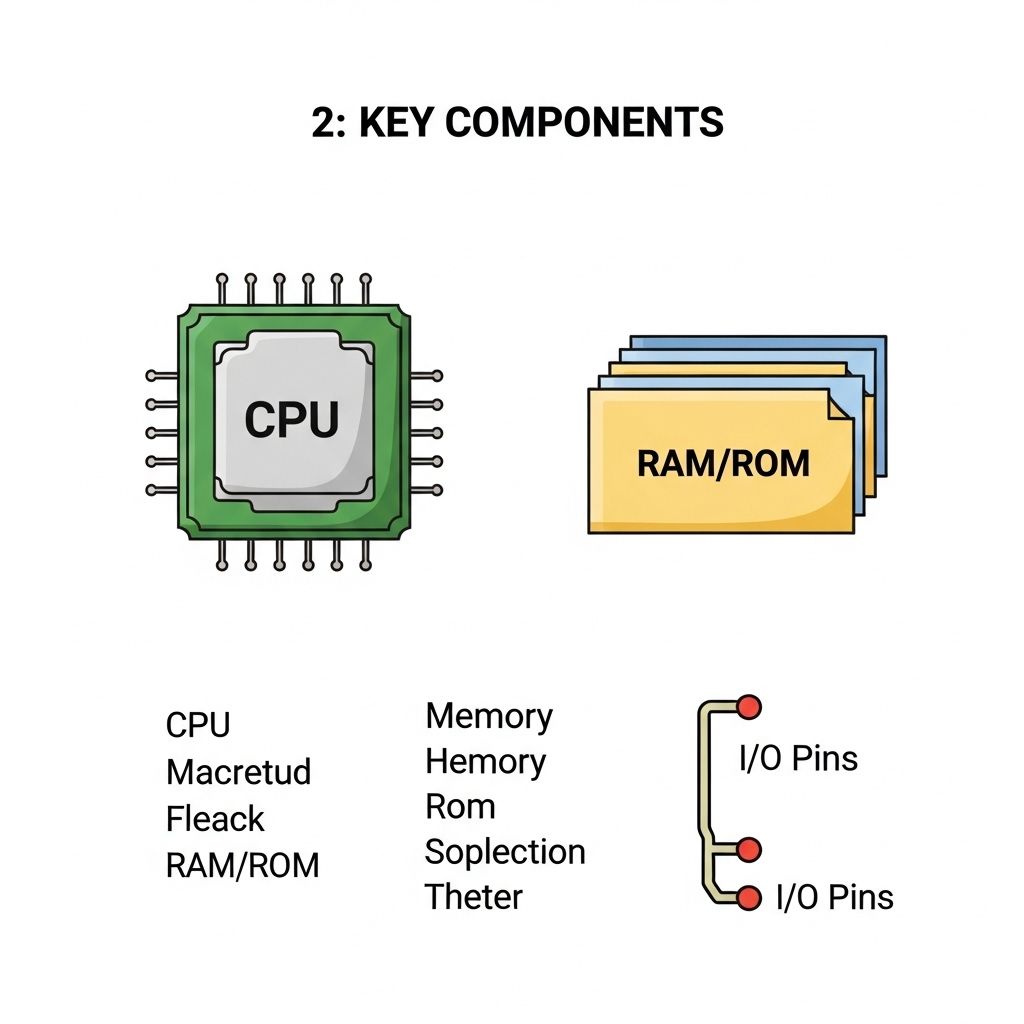
Step 2: Core Components of a Microcontroller
To grasp microcontrollers fully, one must understand their core components:
1. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU is responsible for executing instructions. It interprets commands and processes data, significantly impacting the microcontroller’s performance.
2. Memory
This includes:
- RAM: Temporary storage for data during execution.
- ROM: Permanent storage for firmware and essential code.
- EEPROM: Non-volatile memory for storing data that must persist after power loss.
3. Input/Output Ports
I/O ports enable microcontrollers to interact with other entities.
- Digital I/O: Handles binary signals (high/low).
- Analog I/O: Processes varying voltage levels.
Step 3: Programming Microcontrollers
One of the most exciting aspects of microcontrollers is that they can be programmed to perform specific tasks. Popular programming languages include:
- C/C++
- Assembly Language
- Python (with certain boards like Arduino)
Basic Structure of a Program
Microcontroller programs typically follow a simple structure:
- Initialization: Set up the hardware and configurations.
- Main Loop: Continuously checks for input and executes tasks.
- Interrupts: Handle events that require immediate attention.
Step 4: Development Platforms and Tools
Choosing the right development environment is crucial for effective programming and debugging. Popular platforms include:
- Arduino: User-friendly and great for beginners.
- Raspberry Pi: A versatile platform for advanced projects.
- Microchip MPLAB: Ideal for developing with PIC microcontrollers.
Development Tools
Key tools for microcontroller development include:
- Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)
- Hardware Debuggers
- Simulators
Step 5: Practical Applications
Understanding theory is essential, but applying knowledge is where true mastery lies. Microcontrollers find vast applications across sectors:
1. Consumer Electronics
Microcontrollers power devices like:
- Washing machines
- Smart TVs
- Remote controls
2. Automotive Industry
They also play a significant role in vehicles, including:
- Engine control units
- Airbag systems
- Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS)
3. Robotics
Microcontrollers are fundamental in robotics, controlling:
- Motors and servos
- Sensor data collection
- Decision-making algorithms
Conclusion
By following these five steps, you can gain a solid understanding of microcontrollers and their applications. As technology continues to evolve, mastering microcontrollers will enable you to contribute to innovative solutions, paving the way for advancements in automation and smart technology.
FAQ
What is a microcontroller?
A microcontroller is a compact integrated circuit designed to govern a specific operation in an embedded system, containing a processor, memory, and input/output peripherals.
What are the main components of a microcontroller?
The main components of a microcontroller include the CPU (central processing unit), RAM (random access memory), ROM (read-only memory), input/output ports, timers, and communication interfaces.
How do I choose the right microcontroller for my project?
To choose the right microcontroller, consider factors such as processing power, memory size, number of I/O pins, power consumption, and available peripherals.
What programming languages are commonly used for microcontrollers?
Common programming languages for microcontrollers include C, C++, and assembly language, with C being the most widely used due to its efficiency and control.
What tools do I need to start programming a microcontroller?
To start programming a microcontroller, you need a development board, an integrated development environment (IDE), a programmer or debugger, and relevant libraries or frameworks.
What are some common applications of microcontrollers?
Microcontrollers are used in various applications such as home automation, robotics, automotive systems, medical devices, and consumer electronics.