The fascinating world of chemistry is built upon the interactions of atoms, and at the heart of these interactions lies the concept of chemical bonding. Understanding how atoms combine to form molecules is crucial for advancements in numerous scientific fields, including materials science, biochemistry, and pharmacology. As we look ahead to 2025, the study of chemical bonding continues to evolve, influenced by new technologies and methodologies that allow for deeper insights into atomic interactions.
Types of Chemical Bonds
Chemical bonds can primarily be categorized into three types: ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. Each of these bonds has distinct characteristics and plays a crucial role in the structure and properties of substances.
Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonding occurs when one atom donates an electron to another atom, resulting in the formation of charged ions. This transfer of electrons leads to an electrostatic attraction between the positively charged cation and the negatively charged anion.
Key Characteristics of Ionic Bonds:
- High melting and boiling points due to strong ionic interactions.
- Formation of crystal lattice structures.
- Good electrical conductivity when dissolved in water or molten.
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This type of bond is common among nonmetals and plays a significant role in the formation of organic compounds.
Key Characteristics of Covalent Bonds:
- Lower melting and boiling points compared to ionic compounds.
- Diverse range of molecular geometries.
- Typically, poor electrical conductivity.
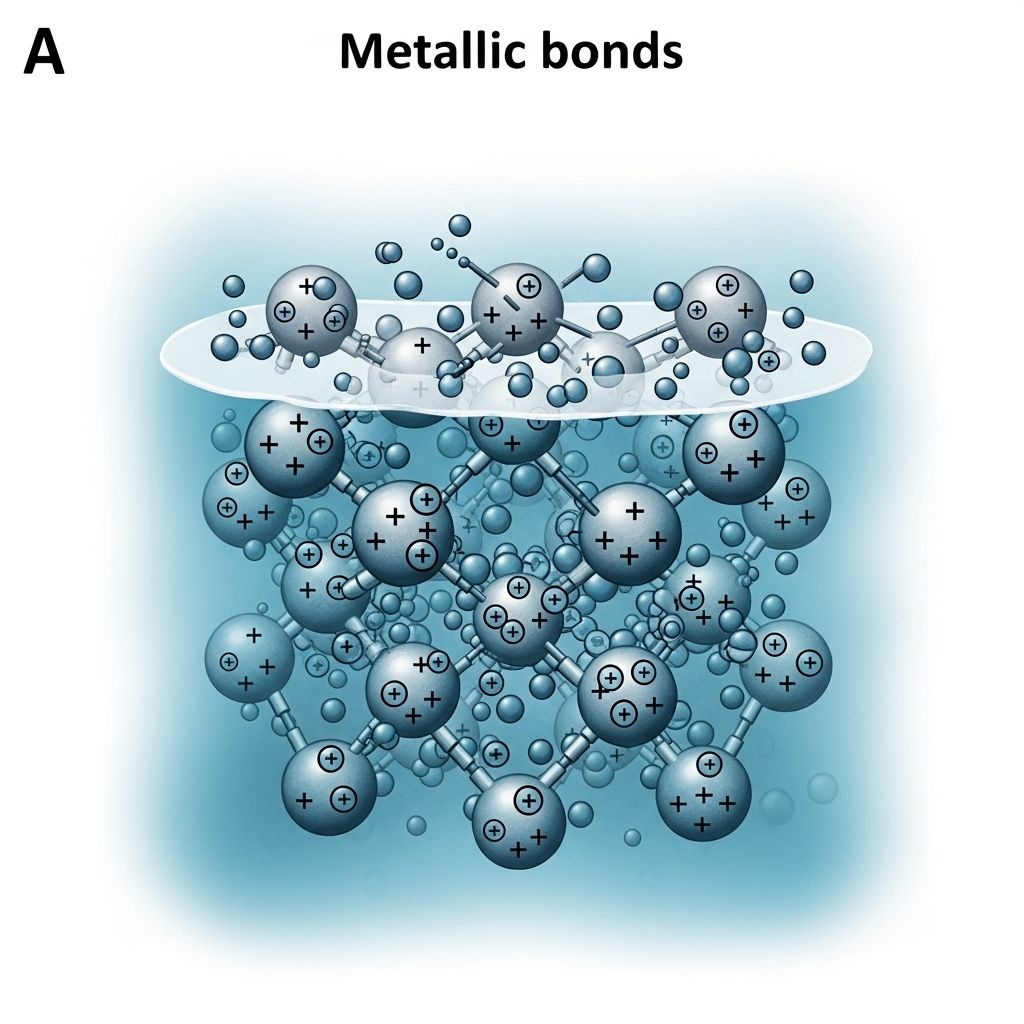
Metallic Bonds
In metallic bonding, electrons are not associated with a single atom but are instead delocalized over a lattice of metal cations. This ‘sea of electrons’ gives metals their characteristic properties.
Key Characteristics of Metallic Bonds:
| Property | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Ductility | Metals can be drawn into wires due to the mobility of electrons. |
| Malleability | Metals can be hammered into thin sheets without breaking. |
| Conductivity | Good conductors of electricity and heat due to free-moving electrons. |
Quantum Mechanics and Chemical Bonding
As we advance into 2025, quantum mechanics remains a fundamental framework for understanding chemical bonding. The quantum nature of electrons and their interactions cannot be fully explained by classical physics, thus necessitating a focus on quantum theories.
Wave-Particle Duality
Electrons exhibit both particle-like and wave-like properties, which are pivotal in defining how they interact and bond with other atoms. The wave functions associated with electrons determine their probable locations around the nucleus and their potential energy states.
Orbital Hybridization
The concept of orbital hybridization explains how atomic orbitals mix to form new hybrid orbitals that can accommodate bonding. This process is essential in understanding the geometry of molecular structures.
Types of Hybridization:
- sp Hybridization: Linear geometry (180° bond angle).
- sp² Hybridization: Trigonal planar geometry (120° bond angle).
- sp³ Hybridization: Tetrahedral geometry (109.5° bond angle).
Emerging Techniques in Chemical Bonding Research
The landscape of chemical bonding research is undergoing transformation, driven by advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and high-throughput experimentation. These innovations are enhancing our ability to predict and analyze chemical bonds with unprecedented accuracy.
Machine Learning in Chemistry
Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast datasets, identifying patterns and relationships that would be challenging to detect through traditional methods. This capability accelerates the discovery of new materials and compounds.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computers operate on principles of quantum mechanics, allowing them to simulate molecular interactions at a level of detail that classical computers struggle to achieve. This capability will profoundly impact the study of chemical bonding, enabling researchers to explore complex systems more effectively.
The Importance of Understanding Chemical Bonds
Grasping the nuances of chemical bonding offers numerous benefits across various disciplines:
In Material Science
A deeper understanding of bonding mechanisms can lead to the development of novel materials with specific properties tailored for applications ranging from electronics to nanotechnology.
In Biochemistry
Insights into molecular bonding can inform drug design and protein engineering, enhancing the efficacy of therapeutic interventions.
In Environmental Chemistry
Understanding chemical bonds aids in the development of strategies for pollution remediation and energy sustainability.
Conclusion
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of chemical bonding, the interplay of classical theories and modern technologies will pave the way for significant breakthroughs. The journey toward a comprehensive understanding of how atoms interact continues to be a vibrant area of study, promising exciting advancements in science and technology going forward.
FAQ
What is chemical bonding?
Chemical bonding is the process by which atoms combine to form molecules or compounds through interactions involving their electrons.
What are the main types of chemical bonds?
The main types of chemical bonds are ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds, each characterized by different interactions between atoms.
How do ionic bonds form?
Ionic bonds form when one atom donates an electron to another atom, resulting in positively and negatively charged ions that attract each other.
What is a covalent bond?
A covalent bond is formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons, allowing them to achieve stable electron configurations.
What role do electrons play in chemical bonding?
Electrons, particularly those in the outer shell of an atom, play a crucial role in determining how atoms bond with one another to form stable compounds.
Why is understanding chemical bonding important?
Understanding chemical bonding is essential for predicting the properties of substances, reactions, and the behavior of materials in various chemical processes.