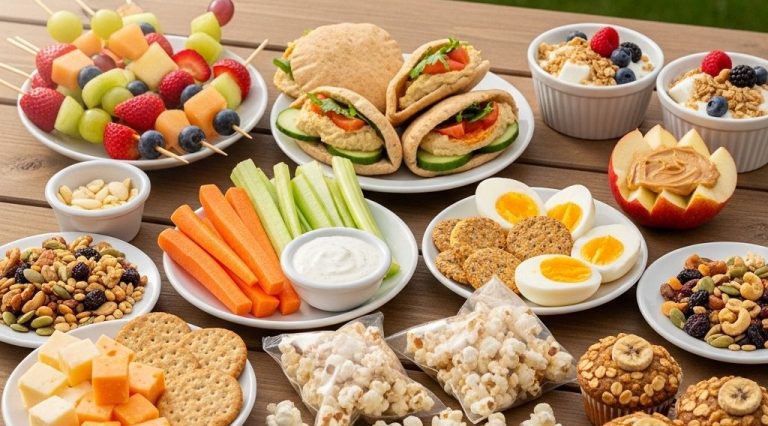
As the popularity of plant-based eating continues to rise in 2025, more people are looking for innovative ways to incorporate veggies and grains into their diets. If you’re just starting, creating a diverse meal plan can make your transition smoother. For those hosting gatherings, exploring printable menu styles can add a touch of creativity and organization to your plant-based dinners.
In recent years, the trend towards plant-based eating has gained significant traction among health enthusiasts, environmental advocates, and culinary adventurers alike. The shift towards a diet centered around whole, plant-derived foods is not just a dietary choice; it’s a lifestyle movement that promotes well-being and sustainability. If you’re intrigued by the idea of adopting a plant-based diet but are unsure where to begin, this article is for you.
The Benefits of Plant-Based Eating
Embracing a plant-based diet can lead to numerous health benefits. Here are some compelling reasons to consider making the switch:
- Improved Nutritional Intake: Plant foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Weight Management: Many plant-based foods are lower in calories, helping with weight control.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: Evidence suggests that a diet high in fruits and vegetables may lower the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Environmental Impact: Plant-based diets usually require fewer resources and result in lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to meat-heavy diets.
- Animal Welfare: Reducing meat consumption can significantly decrease animal suffering and exploitation.
Understanding Plant-Based Diets
Before diving into practical tips, it’s essential to understand what a plant-based diet involves. Contrary to popular belief, plant-based eating does not mean you have to be 100% vegan or vegetarian. Here are different approaches to plant-based diets:
1. Vegan Diet
This strictest form of plant-based eating excludes all animal products, including meat, dairy, eggs, and honey.
2. Vegetarian Diet
Vegetarians avoid meat but may consume dairy products and eggs. There are several subtypes:
- Lacto-vegetarians: Include dairy products.
- Ovo-vegetarians: Include eggs.
- Lacto-ovo vegetarians: Include both dairy and eggs.
3. Flexitarian Diet
This is a semi-vegetarian approach where individuals primarily eat plant-based foods but occasionally consume meat or fish.
Getting Started with Plant-Based Eating
Transitioning to a plant-based diet can feel overwhelming, but with a structured approach, it can be a pleasurable experience. Here are some steps to consider:
Assess Your Current Diet
Take note of what you typically eat and identify areas where you can introduce more plant-based options.
Plan Your Meals
Meal prepping can help simplify your transition. Here’s a simple weekly meal plan template to get you started:
| Day | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Overnight oats with fruit | Quinoa salad | Chickpea curry with rice |
| Tuesday | Smoothie with spinach and banana | Lentil soup | Stuffed bell peppers |
| Wednesday | Avocado toast | Falafel wrap | Stir-fried tofu and veggies |
| Thursday | Chia seed pudding | Vegetable sushi | Black bean tacos |
| Friday | Fruit salad with nuts | Veggie burger | Spaghetti with marinara sauce |
| Saturday | Pancakes with maple syrup | Cucumber and chickpea salad | Cauliflower pizza |
| Sunday | Granola with almond milk | Roasted vegetable bowl | Vegetable stir-fry |
Stock Your Pantry
Fill your kitchen with plant-based staples. Here’s a list of essentials:
- Whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, oats)
- Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, beans)
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds)
- Fruits and vegetables (fresh, frozen, or canned)
- Plant-based oils (olive oil, coconut oil)
- Herbs and spices for flavoring
Creating Delicious Plant-Based Meals
Cooking with plants can be incredibly enjoyable and rewarding. Here are some tips to help you in the kitchen:
Experiment with New Ingredients
Try to discover lesser-known grains, legumes, and vegetables. For instance:
- Quinoa: A high-protein grain that is versatile and delicious.
- Jackfruit: A meat substitute with a texture similar to shredded pork.
- Kale: A nutrient-dense leafy green that can be used in salads, smoothies, or cooked dishes.
Explore Global Cuisines
Cuisines from around the world offer an abundance of plant-based dishes. Here are a few ideas to inspire you:
- Indian: Try dishes like dal, chana masala, or vegetable biryani.
- Mexican: Create tacos with lentils, sautéed peppers, and guacamole.
- Italian: Make a hearty minestrone soup or vegetable risotto.
Navigating Social Situations
Transitioning to a plant-based lifestyle may pose challenges in social settings, but it can be managed gracefully.
Dining Out
Here are a few tips for enjoying meals out:
- Research menus ahead of time to find plant-based options.
- Don’t hesitate to ask the server for modifications to dishes.
- Consider informing your friends or family about your dietary preferences when making plans.
Social Gatherings
Bring your own dish to share, ensuring you have something plant-based to enjoy. This can also introduce others to delicious plant-based options.
Essential Nutrients in a Plant-Based Diet
When shifting to a plant-based diet, pay attention to your nutritional intake to ensure you’re meeting your needs:
1. Protein
Sources include beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, and quinoa.
2. Iron
Plant-based iron sources include lentils, chickpeas, seeds, and fortified cereals. Pair these with vitamin C-rich foods for better absorption.
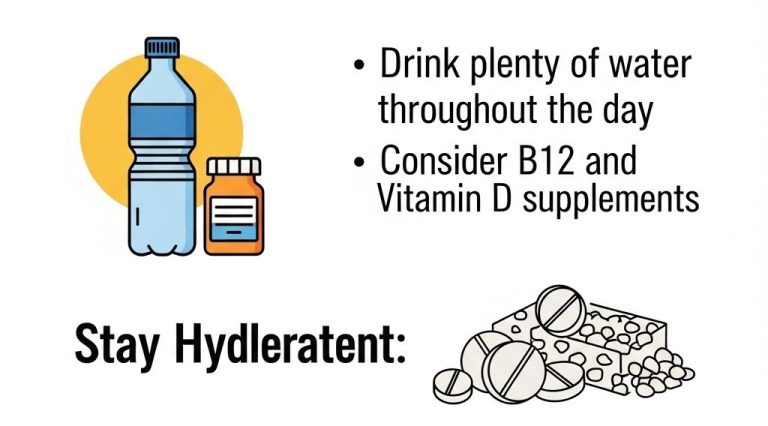
3. Vitamin B12
This vitamin is typically found in animal products, so consider fortified foods or a supplement.
4. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Sources include flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and algae-based supplements.
Overcoming Challenges
Many people face challenges while transitioning to a plant-based diet. Here are some strategies to help you persevere:
1. Cravings for Animal Products
Find plant-based alternatives that satisfy similar textures or flavors. For example, try tempeh bacon or cashew cheese.
2. Lack of Knowledge
Educate yourself through cookbooks, blogs, and documentaries that inspire and inform your journey.
3. Social Pressure
Stay confident in your choices, and surround yourself with supportive individuals who respect your dietary preferences.
Conclusion
Transitioning to a plant-based diet is a journey best approached with curiosity and an open mind. By understanding the benefits, planning meals, and exploring new culinary experiences, you can not only enhance your health but also contribute positively to the environment and animal welfare. So take that first step, and enjoy the flavorful, nutritious adventure that awaits in the world of plant-based eating!
FAQ
What is plant-based eating?
Plant-based eating focuses on foods derived from plants, including fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, while minimizing or eliminating animal products.
What are the health benefits of a plant-based diet?
A plant-based diet can lead to numerous health benefits, including reduced risk of heart disease, lower blood pressure, improved digestion, and enhanced weight management.
How do I start a plant-based diet as a beginner?
Begin by gradually incorporating more plant-based meals into your diet, exploring new recipes, and substituting animal products with plant-based alternatives.
Do I need to take supplements on a plant-based diet?
While a well-planned plant-based diet can provide most nutrients, some individuals may need to consider supplements for Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, and Omega-3 fatty acids.
What are some easy plant-based recipes for beginners?
Easy plant-based recipes include vegetable stir-fries, lentil soups, chickpea salads, and smoothie bowls, which are simple to prepare and packed with nutrients.
Can I eat out on a plant-based diet?
Yes, many restaurants now offer plant-based options. It’s helpful to research menus in advance or ask for modifications to make meals plant-based.