In today’s fast-paced technological landscape, understanding the nuances of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning is crucial. These concepts have significant implications across various industries, similar to how well-crafted bag mockups enable designers to visualize their creations. This article will clarify these interconnected areas and their distinct roles in advancing technology.
The rapid advancement in technology has led to the emergence of various concepts that have transformed industries and everyday life. Among these concepts, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) are often mentioned interchangeably, leading to confusion. In this article, we will dissect the differences and relationships between these three integral components of modern technology.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
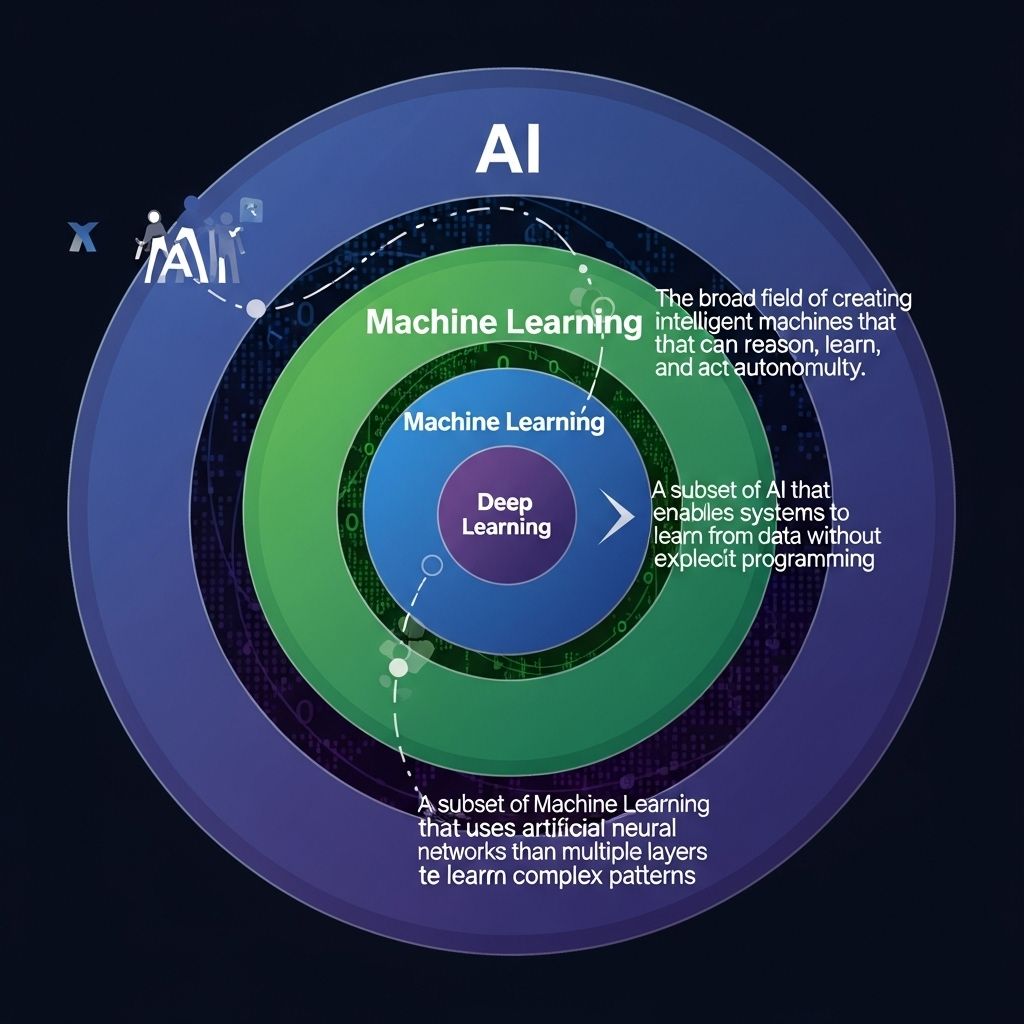
Artificial Intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think, learn, and make decisions like a human. AI encompasses various techniques and technologies, including rule-based systems, natural language processing, and robotics. The goal of AI is to enable machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence.
Types of AI
- Narrow AI: Also known as Weak AI, this type of AI is designed to perform a specific task, such as voice recognition, image processing, or playing a game.
- General AI: Also referred to as Strong AI, this type is still theoretical and aims to replicate human intelligence across a wide range of tasks.
- Superintelligent AI: This concept involves AI that surpasses human intelligence and is capable of outperforming humans in every cognitive task.
Diving into Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on the development of algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make predictions based on data. This area of study leverages statistical methods to enable machines to improve their performance on a task through experience.
How Machine Learning Works
The core idea behind machine learning is to allow a computer to learn from data without being explicitly programmed for every task. Here are the key steps involved:
- Data Collection: Gathering a large dataset relevant to the problem.
- Data Preprocessing: Cleaning and organizing the data to make it suitable for analysis.
- Choosing a Model: Selecting an appropriate algorithm that best suits the task.
- Training the Model: Feeding the model data to help it learn patterns.
- Evaluating the Model: Testing the model on unseen data to assess its accuracy.
- Deployment: Implementing the model for real-world use.
Types of Machine Learning
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Supervised Learning | Algorithms learn from labeled data, making predictions based on input-output pairs. |
| Unsupervised Learning | Algorithms analyze unlabeled data to find patterns or groupings. |
| Reinforcement Learning | Algorithms learn by interacting with an environment and receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties. |
Exploring Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning that utilizes neural networks with many layers (deep neural networks) to analyze various forms of data. It is particularly effective in processing large datasets and is used extensively in applications such as image and speech recognition.
Key Components of Deep Learning
Deep Learning models are built on the following components:
- Neural Networks: Computational models that mimic the way human brains work. They consist of layers of interconnected nodes (neurons).
- Activation Functions: Functions that determine the output of a neuron based on its input, adding non-linearity to the model.
- Backpropagation: A method of updating the weights of the network based on the error of the output compared to the expected result.
Applications of Deep Learning
Deep Learning is making significant inroads across various domains, including:
- Image Recognition
- Natural Language Processing
- Autonomous Vehicles
- Healthcare Diagnostics
- Financial Technology
Comparative Analysis of AI, ML, and DL
To clarify the distinctions between these terms, consider the following comparisons:
| Aspect | Artificial Intelligence | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simulates human intelligence | Subfield of AI focused on learning from data | Subfield of ML using neural networks |
| Data Dependency | Can operate with structured and unstructured data | Requires structured data | Requires large amounts of unstructured data |
| Complexity | Can include simple rule-based systems | Moderate complexity with algorithms | High complexity with multiple layers |
Conclusion
In summary, while Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning are interconnected, they represent different scopes of technology and research. AI is the broadest term encompassing systems that mimic human intelligence, while Machine Learning focuses on data-driven learning processes. Deep Learning, in turn, is a more advanced subset that employs complex architectures to achieve high levels of accuracy in various applications. Understanding these distinctions can empower tech-savvy individuals and organizations to harness these technologies effectively.
FAQ
What is the difference between AI, machine learning, and deep learning?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broadest concept that refers to machines designed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI that focuses on algorithms and statistical models that enable machines to improve their performance on tasks through experience. Deep Learning (DL) is a specialized subset of ML that uses neural networks with many layers to analyze various factors of data.
How does machine learning fit within artificial intelligence?
Machine learning is a key component of artificial intelligence. While AI encompasses all techniques that allow computers to simulate human behavior, machine learning specifically refers to the methods that enable systems to learn from data and improve over time without being explicitly programmed.
What are some examples of deep learning applications?
Deep learning applications include image and speech recognition, natural language processing, autonomous vehicles, and medical diagnosis, where complex patterns in large datasets are analyzed to produce highly accurate predictions and classifications.
Can all AI systems use machine learning?
Not all AI systems utilize machine learning. Some AI systems operate based on predefined rules and logic rather than learning from data. However, machine learning has become a dominant approach within AI due to its flexibility and effectiveness in handling diverse tasks.
Is deep learning better than machine learning?
Deep learning is not inherently better than machine learning; rather, it is suited for specific tasks that involve large amounts of unstructured data. For simpler tasks or smaller datasets, traditional machine learning algorithms may be more efficient and easier to implement.
How do I choose between machine learning and deep learning for my project?
Choosing between machine learning and deep learning depends on the nature of your project. If you have a large dataset and require high accuracy for complex tasks, deep learning may be the best choice. For smaller datasets or simpler problems, traditional machine learning techniques are often more appropriate.