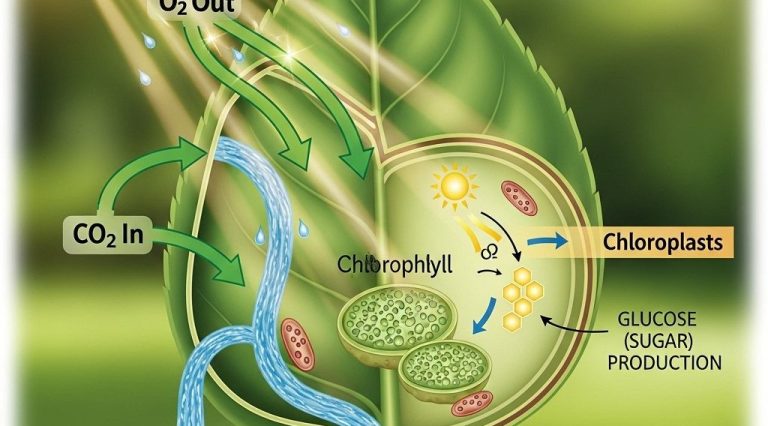
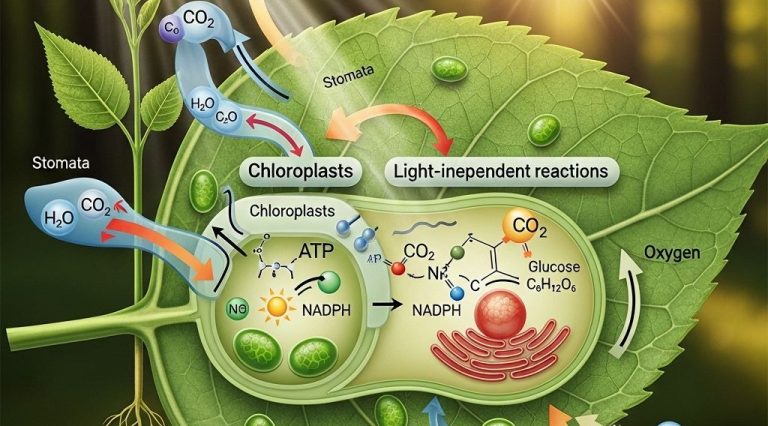
Understanding the core concepts of evolutionary biology is essential for appreciating the intricate web of life on our planet. This field explores how organisms evolve and adapt over time, influencing their interactions with the environment. As you delve into these ideas, consider how different perspectives can shape your understanding, much like integrating custom bottle graphics can enhance a visual project.
Understanding evolutionary biology is crucial for grasping the complexities of life on Earth. This field encompasses various concepts that explain how organisms evolve, adapt, and interact with their environments. Whether you are a student, a researcher, or simply an enthusiast, knowing these essential concepts can deepen your appreciation for the biological world. In this article, we will explore ten fundamental ideas that shape the understanding of evolution.
The Theory of Natural Selection
Natural selection is often considered the cornerstone of evolutionary biology. Proposed by Charles Darwin in the 19th century, this theory explains how species adapt over time. The basic premise is that individuals with traits that improve their survival and reproduction are more likely to pass on those traits to the next generation.
Key Mechanisms of Natural Selection
- Variation: Within any population, individuals exhibit differences in their traits.
- Overproduction: Most species produce more offspring than can survive.
- Survival of the Fittest: Those better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
- Descent with Modification: Over generations, advantageous traits become more common.
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift refers to random changes in allele frequencies within a population. Unlike natural selection, which is a non-random process, genetic drift can lead to significant evolutionary changes over time, particularly in small populations.
Types of Genetic Drift
- Bottleneck Effect: This occurs when a population’s size is drastically reduced, leading to a loss of genetic variation.
- Founder Effect: When a few individuals start a new population, the genetic makeup may not represent the original population.
Mutation
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence of an organism’s genome and are the primary source of genetic variation. While many mutations are neutral or harmful, some can confer beneficial traits that enhance survival.
Types of Mutations
| Type | Description | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Point Mutation | Single nucleotide change | Can be detrimental, neutral, or beneficial |
| Insertion | Extra nucleotides added | Often harmful, can disrupt coding |
| Deletion | Loss of nucleotides | Usually harmful, leads to frameshifts |
Gene Flow
Gene flow, or gene migration, involves the transfer of genetic material between populations. This process can introduce new genetic variation and counteract the effects of genetic drift.
Importance of Gene Flow
- Maintains genetic diversity within populations.
- Reduces the likelihood of speciation.
- Can lead to the spread of advantageous traits.
Speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process where new biological species arise. It can occur through various mechanisms, typically categorized into allopatric and sympatric speciation.
Types of Speciation
- Allopatric Speciation: Occurs when populations are geographically isolated.
- Sympatric Speciation: Happens when populations diverge while inhabiting the same area, often through polyploidy in plants or behavioral differences in animals.
Coevolution
Coevolution refers to the reciprocal evolutionary changes that occur between interacting species. These relationships can drive significant adaptations in both parties.
Examples of Coevolution
- Predator-Prey Relationships: As predators evolve better hunting strategies, prey species may develop enhanced defenses.
- Mutualism: Species that benefit from each other’s existence, such as flowering plants and their pollinators, often influence each other’s evolution.
Extinction
Extinction is a natural part of evolution, representing the end of a species. However, human activities have accelerated extinction rates, leading to biodiversity loss.
Causes of Extinction
- Habitat destruction
- Climate change
- Overexploitation
- Invasive species
Adaptive Radiation
Adaptive radiation is the rapid evolution of diversely adapted species from a common ancestor. This phenomenon often occurs when species colonize new environments with various niches.
Examples of Adaptive Radiation
- The Darwin’s finches in the Galápagos Islands.
- The diversification of mammals after the extinction of dinosaurs.
Evolutionary Developmental Biology (Evo-Devo)
Evo-Devo is an interdisciplinary field that studies the relationship between development and evolution. It examines how changes in developmental processes can lead to evolutionary changes.
Key Concepts in Evo-Devo
- Homologous structures: Similar structures arising from a common ancestor.
- Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny: The idea that embryonic development can reflect evolutionary history.
Conclusion
The concepts outlined in this article represent just a glimpse into the rich and intricate tapestry of evolutionary biology. From natural selection to the nuances of genetic drift, these ideas are fundamental to understanding the dynamics of life on Earth. As our world continues to change, appreciating evolution’s role in shaping biodiversity is more important than ever.
FAQ
What are the essential concepts in evolutionary biology?
The essential concepts include natural selection, genetic drift, mutation, gene flow, speciation, adaptation, evolutionary fitness, common descent, phylogenetics, and coevolution.
How does natural selection work?
Natural selection works by favoring individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproduction, leading to those traits becoming more common in the population over generations.
What is genetic drift and its significance?
Genetic drift is the random change in allele frequencies in a population, which can lead to significant evolutionary changes, especially in small populations.
What role do mutations play in evolution?
Mutations introduce new genetic variations into a population, providing the raw material for evolution by creating new traits that may be subject to natural selection.
What is speciation and how does it occur?
Speciation is the process by which new species arise, typically through mechanisms such as geographic isolation, reproductive isolation, and genetic divergence.
How do adaptations arise in species?
Adaptations arise through the process of natural selection, where advantageous traits improve an organism’s chances of survival and reproduction in its environment.