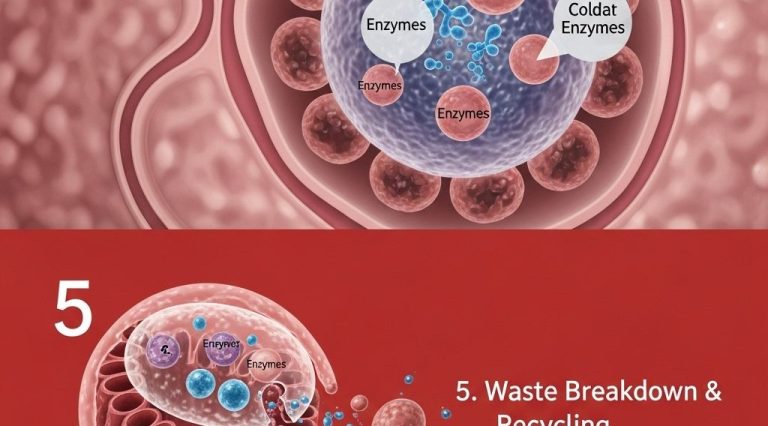
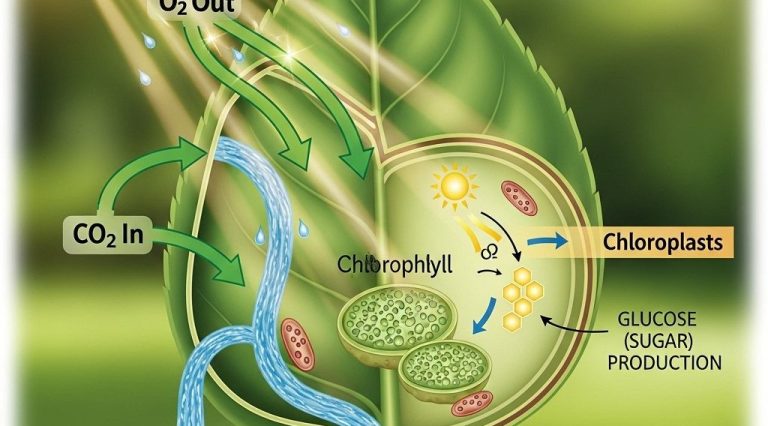
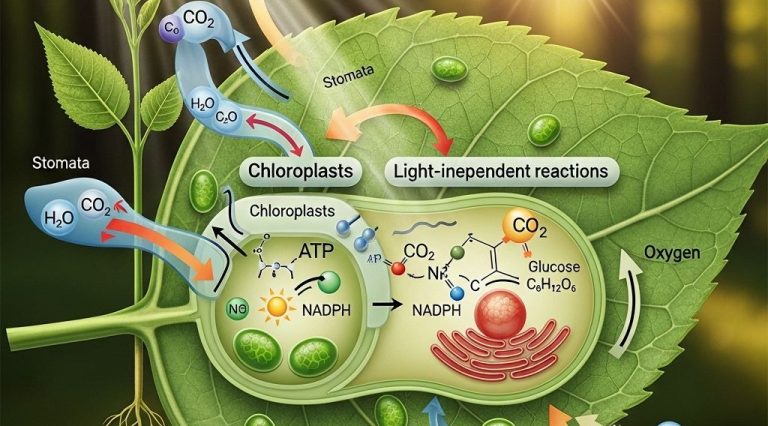
As we delve into the intricacies of cell structure in this article, it’s essential to understand how visual representations can enhance our grasp of biological concepts. Utilizing tools that provide high-quality bag visuals can aid researchers and educators in conveying complex information effectively.
The study of cell structure has always been a cornerstone of biology, laying the groundwork for our understanding of life at the microscopic level. As we enter 2025, advancements in technology and scientific methods have opened new frontiers in cellular research, leading to deeper insights into the complexities of life forms. This article explores the latest developments in cell structure analysis, highlighting innovative approaches, emerging technologies, and the implications of these findings on various fields such as medicine, genetics, and biotechnology.
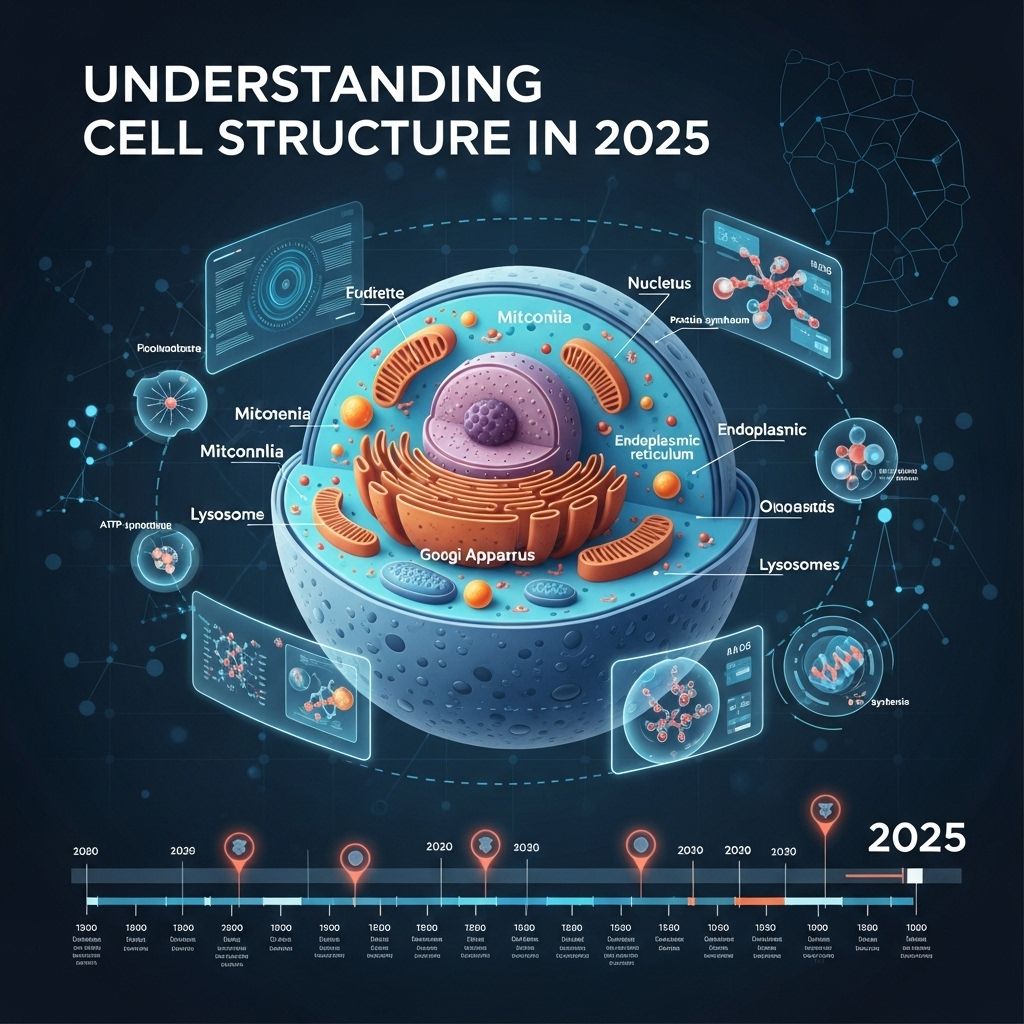
The Basics of Cell Structure
Cells are the fundamental units of life, serving as the building blocks for all living organisms. Understanding cell structure involves examining various components, including:
- Cell Membrane: The outer layer that protects the cell and regulates what enters and exits.
- Cytoplasm: The gel-like substance within the cell that houses organelles.
- Organelles: Specialized structures within a cell that perform distinct functions.
- Nucleus: The control center of the cell, containing genetic material.
Cells are broadly categorized into two types:
- Prokaryotic Cells: Simple, unicellular organisms lacking a nucleus, such as bacteria.
- Eukaryotic Cells: Complex cells with a defined nucleus and organelles, found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Recent Advances in Cell Imaging Techniques
Recent advancements in imaging technology have revolutionized how scientists visualize and study cellular structures.
1. Super-Resolution Microscopy
This technique allows researchers to observe cellular components at resolutions previously thought impossible. By overcoming the diffraction limit of light, super-resolution microscopy provides detailed views of:
- Protein interactions
- Subcellular structures
- Cellular processes in real-time
2. Electron Microscopy
Electron microscopy (EM) offers unparalleled resolution by using electrons instead of light to create images of biological samples. Key types include:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) | Allows visualization of internal cell structure at a molecular level. |
| Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) | Provides 3D images of cell surfaces. |
3. Live Cell Imaging
Live cell imaging enables the observation of living cells over time, offering insights into:
- Cell dynamics and behavior
- Cell division and growth patterns
- Cellular response to stimuli
Insights from Genomic Studies
With advancements in genomics, scientists are now able to explore cell structure at a genetic level. High-throughput sequencing technologies facilitate the analysis of:
- Gene Expression: Understanding how genes contribute to cellular functions and structures.
- Cell Lineage: Tracing the developmental path of cells from embryonic stages to mature forms.
- Single-Cell Genomics: Analyzing the genetic material of individual cells to uncover heterogeneity within cell populations.
Applications in Medicine
These advancements have profound implications for various medical fields, including:
- Cancer Research: Identifying mutations and understanding tumor microenvironments.
- Regenerative Medicine: Tailoring therapies based on specific cell types and their functions.
- Personalized Medicine: Developing treatments based on individual genetic profiles, improving therapeutic efficacy.
Innovative Technologies Shaping Cell Research
As we look forward, several emerging technologies are set to transform cell research even further.
1. CRISPR-Cas9 Technology
This revolutionary gene-editing tool allows scientists to modify DNA with precision. Applications include:
- Correcting genetic defects
- Studying gene function
- Creating models for diseases
2. Artificial Intelligence in Cell Analysis
AI algorithms are being employed to analyze complex datasets, helping researchers to:
- Identify patterns in cell behavior
- Predict cellular responses to drugs
- Automate image analysis
3. 3D Cell Culture Systems
Moving beyond traditional 2D cultures, 3D systems provide a more accurate representation of cellular environments, leading to:
- Improved drug testing models
- Better understanding of tissue architecture
- Insights into cell-cell interactions
The Future of Cell Structure Research
The landscape of cell structure research is rapidly evolving. As we move through 2025 and beyond, the integration of multidisciplinary approaches will pave the way for groundbreaking discoveries. Potential research directions include:
- Integrative Cell Biology: Combining genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics for a holistic understanding of cells.
- Microbiome Studies: Investigating how interactions with microbiota influence cell health and disease.
- Bioengineering: Developing synthetic cells or organoids to study complex biological systems in vitro.
Conclusion
Understanding cell structure is not just a fundamental aspect of biology; it is a dynamic field with vast implications for science and medicine. As technology continues to advance, the insights gained from studying cells will undoubtedly lead to transformative breakthroughs that enhance our understanding of life and improve human health.
FAQ
What are the basic components of a cell?
The basic components of a cell include the cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and organelles such as mitochondria, ribosomes, and endoplasmic reticulum.
How do cells communicate with each other?
Cells communicate with each other through various signaling molecules, such as hormones and neurotransmitters, which bind to receptors on target cells to elicit a response.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane serves as a protective barrier, regulating what enters and exits the cell, and plays a crucial role in cell signaling and communication.
What advancements have been made in cell biology by 2025?
By 2025, advancements in cell biology include improved imaging techniques, CRISPR gene editing applications, and a deeper understanding of cellular processes through artificial intelligence.
How do cellular structures contribute to cell function?
Cellular structures are specialized for specific functions; for example, mitochondria produce energy, while the endoplasmic reticulum synthesizes proteins and lipids, ensuring efficient cellular operation.
What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and various organelles, allowing for greater complexity in function and organization.