The Internet is a complex system that connects devices through various networks, enabling instantaneous communication and information sharing. To illustrate the interconnectedness of digital design, consider exploring certificate layout examples which can provide insights into how design elements work harmoniously in digital platforms.
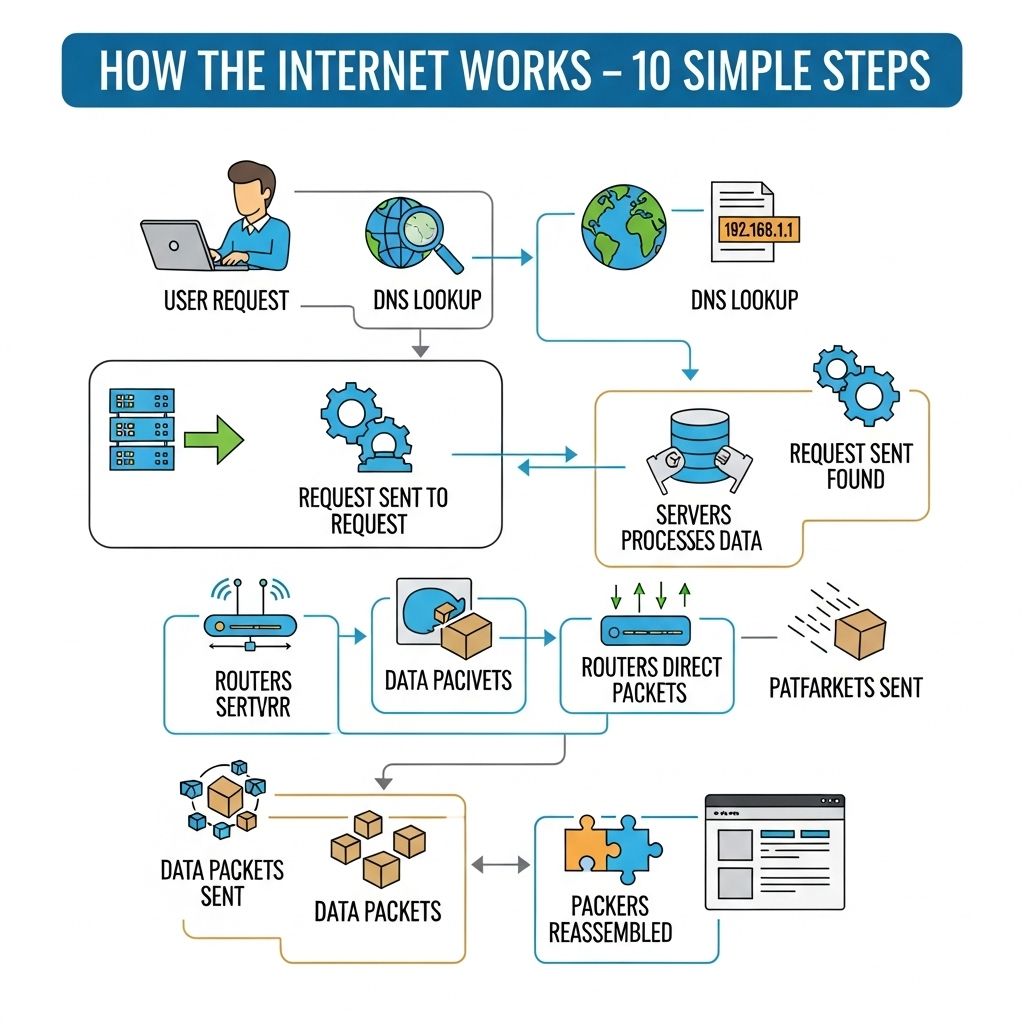
The Internet is often described as a vast network of networks, connecting millions of devices worldwide. Understanding how it operates is crucial in today’s digital age, where information flows at the speed of light. This article simplifies the complex processes behind the Internet into ten straightforward steps, allowing tech-savvy readers to grasp its inner workings.
1. Devices Connect to the Internet
The journey begins with devices such as computers, smartphones, and tablets connecting to the Internet through various means:
- Wired Connections: Ethernet cables link devices to routers and modems.
- Wireless Connections: Wi-Fi signals allow devices to connect without physical cables.
- Mobile Networks: Cellular data (3G, 4G, 5G) provides Internet access on-the-go.
2. Local Networks
Once connected, devices become part of a local area network (LAN). LANs can be found in homes, offices, and public spaces, enabling multiple devices to communicate with each other and access the Internet through a central router.
3. Routers and Modems
Routers and modems play critical roles in Internet connectivity:
| Device | Function |
|---|---|
| Router | Directs data packets between devices on the LAN and the wider Internet. |
| Modem | Modulates and demodulates signals for analog transmission over telephone or cable lines. |
4. Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
ISPs connect users to the Internet. They provide access through various technologies, including:
- DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
- Cable broadband
- Fiber-optic connections
- Satellite
5. Data Transmission
When you send or request data (like loading a webpage), the information is broken down into smaller packets. This process involves:
- Packet Switching: Data is divided into packets, each with sender and receiver addresses.
- Routing: Packets are sent through various networks, following the most efficient paths.
6. Domain Name System (DNS)
Humans prefer easy-to-remember website addresses, while computers communicate using IP addresses. DNS acts as a translator:
- When you enter a website name, DNS servers convert it into an IP address.
- This IP address directs your request to the appropriate server hosting the website.
7. Web Hosting
Web hosting services store web content and make it accessible over the Internet. Key points include:
- Servers: Powerful computers store websites and handle requests.
- Data Centers: Facilities housing multiple servers for redundancy and reliability.
- Types of Hosting: Shared, VPS, dedicated, and cloud hosting options cater to different needs.
8. Web Browsers
Your device uses web browsers (like Chrome, Firefox, Safari) to access and display web content. These applications do the following:
- Request web pages by sending HTTP/HTTPS requests.
- Render HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to present information visually.
- Cache data to improve load times on repeat visits.
9. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
To enhance performance and speed, many websites utilize CDNs. These networks consist of multiple servers located globally that:
- Store copies of web content close to users, reducing latency.
- Distribute traffic to prevent overload on a single server.
10. Security Protocols
Finally, security measures are vital for safe Internet usage. Key protocols include:
- HTTPS: Encrypts data between the browser and server, ensuring privacy.
- Firewalls: Protect networks from unauthorized access.
- VPNs: Provide secure, encrypted connections for remote users.
Conclusion
Understanding how the Internet works not only demystifies a crucial aspect of modern life but also empowers users to navigate the digital landscape confidently. By grasping these ten simple steps, you can appreciate the intricacies behind your everyday online interactions, making you a more informed and savvy Internet user.
FAQ
What is the basic principle of how the internet works?
The internet works by connecting millions of computers through a network of servers, allowing them to communicate with each other using standardized protocols.
How does data transfer occur on the internet?
Data transfer on the internet occurs through packets that are sent over various routes, using protocols like TCP/IP to ensure reliable delivery.
What role do IP addresses play in internet connectivity?
IP addresses serve as unique identifiers for each device connected to the internet, allowing them to send and receive data accurately.
How do web browsers interact with servers?
Web browsers send requests to servers using HTTP or HTTPS protocols, which then respond by sending back the requested web pages.
What is the purpose of domain names?
Domain names provide a human-readable address for websites, making it easier for users to navigate the internet instead of using numerical IP addresses.
How does the internet ensure data security?
The internet employs various security measures, including encryption, firewalls, and SSL certificates, to protect data during transmission.