In the competitive landscape of plugin development, understanding effective strategies is crucial for success. Just as utilizing high-quality book mockups can enhance your product’s presentation, applying the right monetization approaches can significantly boost your earning potential. This guide will provide you with comprehensive insights on building plugins that can consistently generate revenue.
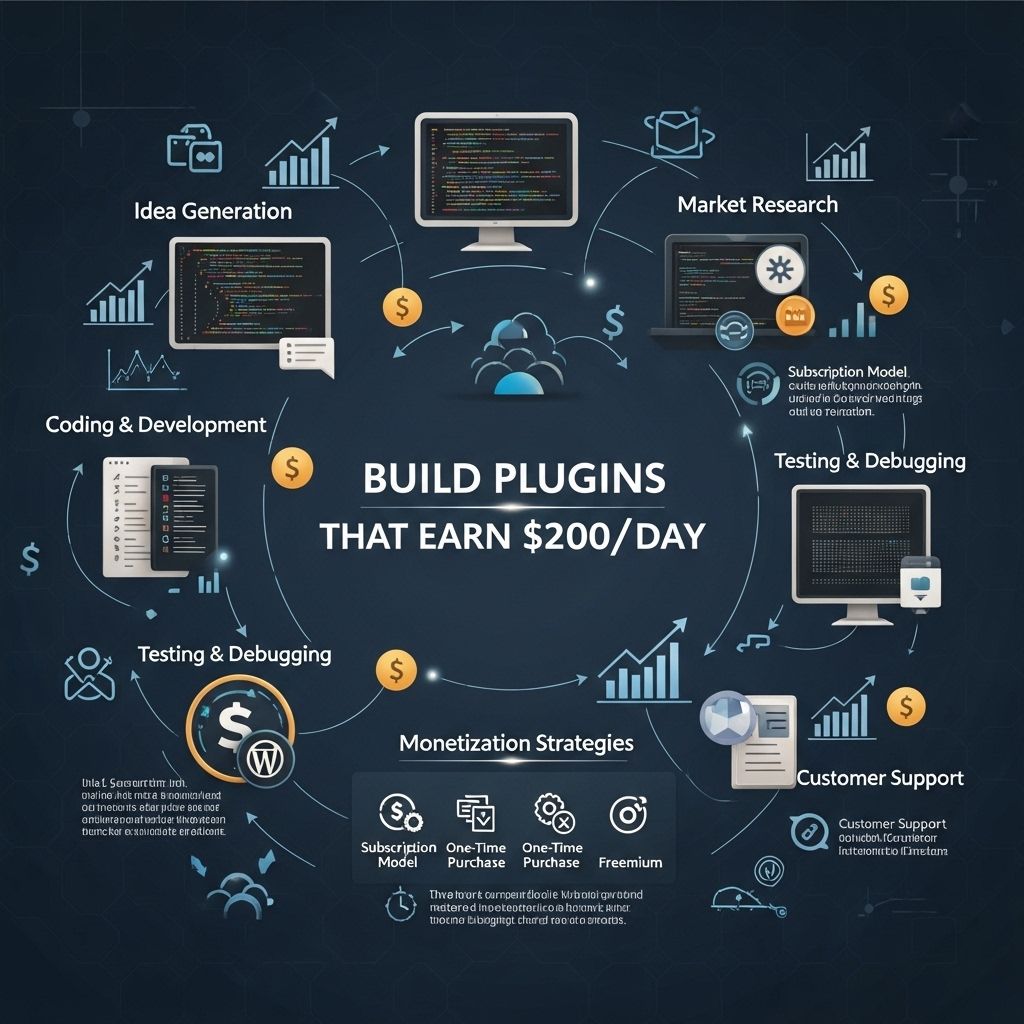
The world of plugin development offers a lucrative opportunity for tech-savvy individuals looking to monetize their skills. With the right strategies and tools, it’s entirely possible to build plugins that can generate consistent income, sometimes even reaching $200 a day. This article will delve into the essential steps, tips, and considerations needed to create successful plugins, while also exploring how to market them effectively.
Understanding the Plugin Market
Before diving into development, it’s crucial to understand the market landscape. Identifying the right niche can significantly impact your potential earnings.
Types of Plugins
Plugins can be categorized in various ways depending on the platforms they are built for. Here are some common types:
- WordPress Plugins: Enhance functionality for websites.
- Browser Extensions: Improve user experience on browsers like Chrome and Firefox.
- Software Add-ons: Improve the capabilities of popular software like Photoshop or Visual Studio.
- Game Mods: Modify gameplay experiences for popular video games.
Research and Planning
Once you have a grasp on the types of plugins available, the next step is to research and plan your product.
Identifying Pain Points
Successful plugins often address specific pain points. Here are some methods to identify these:
- Conduct surveys in relevant online communities.
- Analyze reviews of existing plugins to find common complaints.
- Utilize keyword research tools to discover what users are searching for.
Market Analysis
After identifying potential pain points, performing a thorough market analysis is essential. This involves:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Competitors | Analyze leading plugins in your chosen category. |
| Pricing Models | Determine how similar plugins are priced. |
| Target Audience | Identify who your ideal users are. |
Development Process
With a solid understanding of the market, you can embark on the development process.
Choosing the Right Tools
Depending on the type of plugin you’re building, the tools will vary. Here are some commonly used frameworks:
- WordPress: PHP, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Browser Extensions: HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and specific APIs.
- Game Mods: Programming languages pertinent to the game engine.
Development Steps
Follow these essential steps during development:
- Set up your development environment.
- Develop core functionalities.
- Implement user interface designs.
- Conduct thorough testing and debugging.
Launching the Plugin
After development, prepare for launch. Here’s a checklist for a successful release:
- Create comprehensive documentation.
- Prepare marketing materials, including screenshots and demo videos.
- Test across various platforms and devices.
Monetization Strategies
To earn $200 a day from your plugins, you’ll need to implement effective monetization strategies.
Freemium Model
Offer a free version of your plugin with limited features, and charge for premium features. This model can build a user base quickly.
One-Time Purchase
This straightforward method involves selling the plugin for a one-time fee. Ensure that the value justifies the price.
Subscription-Based Model
Charge users a monthly or yearly fee for access to your plugin. This model ensures a recurring revenue stream.
Affiliate Marketing
Partner with other companies or products that complement your plugin, earning commissions for referrals.
Marketing Your Plugin
Creating an outstanding plugin is only part of the equation. Effective marketing is crucial for sales.
Building a Website
A dedicated website serves as a central hub for your plugin. This should include:
- Product description
- Testimonials
- Blog for SEO and engagement
- Contact and support sections
Using Social Media
Engage with potential users on platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and LinkedIn. Share valuable content and updates about your plugin.
Content Marketing
Write blog posts or create videos that provide value to your audience, subtly promoting your plugin within the content.
Influencer Partnerships
Collaborate with influencers in your niche to reach a broader audience. They can help validate your plugin to their followers.
Building a Support Network
Providing excellent customer support can enhance user satisfaction and retention. Consider these methods:
- Create a dedicated support forum.
- Offer personalized email support.
- Utilize chatbots for immediate responses.
Scaling Your Business
Once your plugin starts generating income, consider scaling your business:
- Develop additional plugins.
- Expand into other platforms or markets.
- Hire team members to assist with development and support.
Conclusion
Building plugins that can earn substantial income requires a combination of market knowledge, technical skills, and marketing strategies. By focusing on user needs, delivering high-quality products, and effectively promoting your work, you can carve out a successful niche in the plugin market. With dedication and the right approach, reaching $200 per day is an achievable goal.
FAQ
What are plugins and how do they work?
Plugins are software components that add specific features or functionalities to an existing computer program, enhancing its capabilities without altering the core structure.
How can I create a plugin that generates income?
To create a profitable plugin, identify a target audience’s pain points, develop a solution, and monetize it through sales, subscriptions, or advertisements.
What platforms can I build plugins for to earn money?
You can build plugins for popular platforms like WordPress, Shopify, WooCommerce, and various content management systems that support third-party extensions.
What strategies can I use to market my plugins effectively?
Utilize social media marketing, SEO, content marketing, and partnerships with influencers or bloggers to promote your plugins and reach a wider audience.
How can I determine the pricing for my plugin?
Research competitor pricing, analyze the value your plugin offers, and consider a pricing model that aligns with your target audience’s willingness to pay.
What are the common mistakes to avoid when building plugins?
Avoid neglecting user feedback, underestimating support needs, and failing to optimize for performance and compatibility with other software.