As the digital landscape evolves, agile teams must prioritize security to effectively navigate the complexities of cloud-native architectures. Understanding key practices, such as the implementation of continuous monitoring and automated assessments, can enhance resilience against threats. For teams exploring innovative ideas to promote their offerings, consider checking out promotional bag ideas that can seamlessly integrate into your strategies.
As organizations increasingly embrace cloud-native technologies, the need for robust security measures tailored to agile teams has never been more critical. By 2025, the landscape of cloud-native security will evolve, driven by the rapid pace of innovation, the growing complexity of deployments, and the heightened sophistication of cyber threats. This article explores the future of cloud-native security, focusing on practices that enable agile teams to innovate confidently while maintaining a strong security posture.
The Rise of Cloud-Native Architectures
Cloud-native architectures are becoming the standard for modern application development. They enable organizations to build and run scalable applications in dynamic environments, such as public, private, and hybrid clouds. Key characteristics of cloud-native architectures include:
- Microservices: Applications are broken down into smaller, independent services that can be deployed and scaled independently.
- Containerization: Using containers (e.g., Docker) allows developers to package applications and their dependencies into a single unit, ensuring consistency across various environments.
- Orchestration: Tools like Kubernetes manage the deployment, scaling, and operation of containerized applications.
- DevOps Practices: Agile development and deployment processes that promote collaboration between development and operations teams.
Challenges in Cloud-Native Security
As organizations transition to cloud-native environments, they face several security challenges:
- Increased Attack Surface: The distributed nature of microservices increases potential entry points for attackers.
- Dynamic Environments: The ephemeral nature of cloud resources complicates visibility and management of security policies.
- Configuration Errors: Misconfigurations in cloud services can lead to significant vulnerabilities.
- Third-Party Dependencies: Relying on numerous external libraries and services increases the risk of introducing vulnerabilities.
Key Security Practices for Agile Teams
To effectively secure cloud-native applications, agile teams should adopt the following best practices:
1. Shift Left: Integrate Security Early
Incorporating security into the development lifecycle from the beginning, known as ‘shifting left,’ ensures that security is not an afterthought. This can be accomplished by:
- Conducting regular threat modeling sessions during the design phase.
- Implementing security testing tools in CI/CD pipelines to identify vulnerabilities before deployment.
- Educating developers on secure coding practices and common vulnerabilities.
2. Embrace Automation
Automation is critical for maintaining security in agile environments. Automated tools can:
- Perform continuous security assessments of code and applications.
- Enforce security policies automatically across the deployment pipeline.
- Manage secrets and credentials securely without manual intervention.
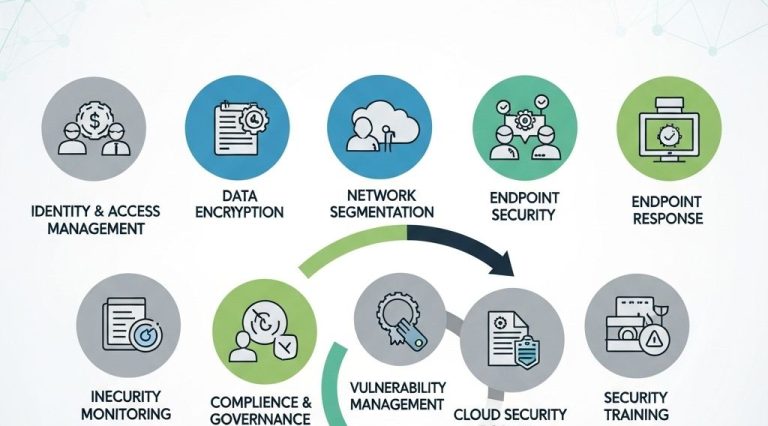
3. Implement Least Privilege Access
Limiting access to resources is vital for minimizing potential damage in case of a breach. Agile teams should:
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) to grant permissions based on the principle of least privilege.
- Regularly review and update access permissions as team members and project needs change.
- Utilize network segmentation to isolate sensitive components of applications.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Logging
Maintaining visibility into cloud-native environments is essential for detecting and responding to threats. Agile teams should implement:
- Centralized logging to aggregate logs from all services and applications.
- Real-time monitoring tools to detect anomalies and potential security incidents.
- Regular reviews of logs for identifying unauthorized access or other suspicious activities.
Emerging Technologies in Cloud-Native Security
As we look towards 2025, several emerging technologies will play a significant role in enhancing cloud-native security:
1. AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will be instrumental in identifying patterns and anomalies that indicate security threats. By analyzing vast amounts of data, these technologies can:
- Predict potential vulnerabilities based on historical attack patterns.
- Automatically respond to security incidents in real-time.
- Enhance threat intelligence by correlating data from various sources.
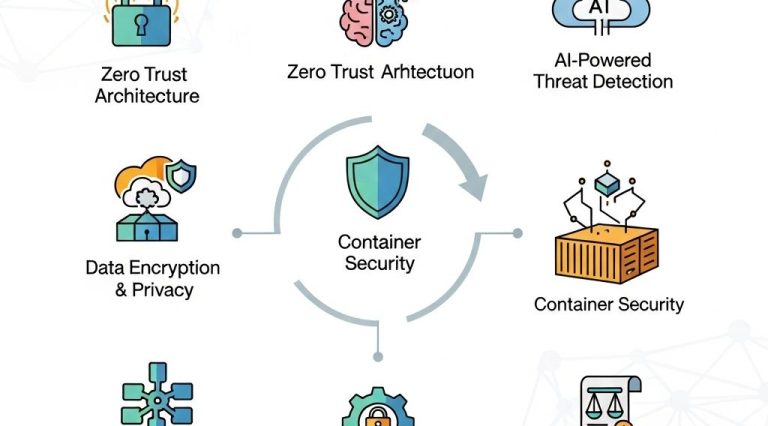
2. Zero Trust Architecture
The Zero Trust model assumes that threats can exist both inside and outside the network perimeter. This approach requires:
- Continuous verification of user identities and device health.
- Micro-segmentation of networks to contain potential breaches.
- Contextual access policies that adapt based on user behavior and risk levels.
3. Serverless Security Solutions
Serverless computing reduces infrastructure management overhead but introduces unique security challenges. Organizations must focus on:
- Securing serverless functions against vulnerabilities in third-party libraries.
- Implementing runtime protection mechanisms to monitor function behavior.
- Using automated tools to analyze serverless architectures for security misconfigurations.
Fostering a Security-First Culture
For agile teams to successfully navigate the complexities of cloud-native security, fostering a culture that prioritizes security is essential. This includes:
- Training and Awareness: Regular training sessions on security best practices for all team members.
- Collaboration: Encouraging open communication between development, operations, and security teams.
- Ownership: Assigning security responsibilities to specific team members to ensure accountability.
Conclusion
As we approach 2025, the importance of cloud-native security for agile teams will only grow. By embracing best practices, leveraging emerging technologies, and fostering a culture of security, organizations can confidently innovate and adapt in an increasingly cloud-centric world. Ultimately, the success of cloud-native applications will depend on the ability to balance agility with robust security measures, ensuring that teams can deliver value without compromising on safety.
FAQ
What is cloud-native security?
Cloud-native security refers to security practices and tools specifically designed to protect applications and data in cloud environments, leveraging the unique capabilities of cloud computing.
How can agile teams implement cloud-native security in 2025?
Agile teams can implement cloud-native security by integrating security into the DevOps pipeline, automating security testing, and utilizing security tools that are built for cloud environments.
What are the key benefits of cloud-native security for agile teams?
The key benefits include improved speed and flexibility, enhanced visibility into security risks, and the ability to scale security measures alongside application development.
What challenges do agile teams face with cloud-native security?
Challenges include managing the complexity of cloud environments, ensuring compliance with regulations, and maintaining security across rapidly changing applications.
What tools are essential for cloud-native security in 2025?
Essential tools include cloud security posture management (CSPM), container security solutions, and runtime application self-protection (RASP) tools.
How does automation play a role in cloud-native security for agile teams?
Automation helps agile teams streamline security processes, reduce human error, and ensure continuous compliance and monitoring throughout the development lifecycle.